Sat, Feb 21, 2026
[Archive]
Volume 2, Issue 1 (7-2004)
IJRM 2004, 2(1): 1-8 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Kahraman S, Findikli N. Current Status of Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis. IJRM 2004; 2 (1) :1-8
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-16-en.html
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-16-en.html
Full-Text [PDF 311 kb]
(787 Downloads)
| Abstract (HTML) (3574 Views)
Full-Text: (627 Views)
Introduction
It has been reported that nearly 50% of the cases with early pregnancy loss contain chromosomal abnormalities (Chandley 1984; Zenzes and Casper 1992; Jacobs ve Hassold 1995; Jobanputra et al., 2002). Although most of them are found to be eliminated before implantation, some anomalies such as trisomies of chromosomes 13, 18 and 21 can reach to blastocyst stage and even result in affected offspring (Sandalinas et al., 2001). Chromosomal aneuploidy has also been shown to increase under inappropriate stimulation protocols, suboptimal culture conditions, paternal factors and lack of certain growth factors (Munne et al., 1995; Janny and Menezo 1996; Kaye 1997; Moor et al., 1998; Calogero et al., 2003; Findikli et al., 2004).
Screening preimplantation embryos for certain chromosomal abnormalities is generally termed as PGD for aneupoloidy screening (PGD-AS). It is based on the principle that detection and elimination of chromosomally abnormal embryos before embryo transfer could increase the reproductive efficiency in certain cases where aneuploidy is proven or likely to exert a negative effect (Munne et al., 1995; Benadiva et al., 1996; Kuliev et al., 2002). So far, applications of PGD for aneuploidy screening to a large extent involved indications such as advanced maternal age, repeated implantation failures and recurrent abortion (Munne et al., 1999; Gianaroli et al., 2001; Kuliev et al., 2002; Munne 2002; Wilton 2002; Pehlivan et al., 2003; Rubio et al., 2003; Kahraman et al., 2004a). Due to their increased risk of producing aneuploid gamete cells, carriers of structural abnormalities such as inversions and translocations are also among other PGD candidates.
Improved clinical outcome with decreased early abortions after selection of abnormal embryos with PGD have recently been reported by different groups on reciprocal and Robertsonian translocations (Conn et al., 1998; Scriven et al., 1998, 2000; Munne et al., 1998, 2000; Findikli et al., 2003). Furthermore, the positive effect of PGD application on clinical results was recently documented in severe male infertility, Klinefelter’s syndrome and cases with abnormal gamete cell morphology, which are among other potential PGD indications (Gianaroli et al., 2001; Kahraman et al., 2000; 2003, 2004a, 2004b; Aran et al., 2004;). The data accumulated on approximately 5000 PGD cycles having above indications clearly shows that the prevalence of chromosomal abnormalities in oocytes as well as at cleavage stages can be as high as 50-70%. Elimination of such embryos prevents the birth of a trisomic child, decreases the abortion as well as high order pregnancy rates and has a positive impact on implantation, validating the beneficial approach of selecting euploid embryos for embryo transfer in PGD for certain indications (IWGPG 2001; Munne et al., 2003; Kuliev and Verlinsky 2004a).
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis for single gene disorders
If one or both partners are carriers of a genetic disease, in order to prevent the birth of an affected offspring, preimplantation embryos can be screened for a known genetic defect. Up to date, more than 300 healthy children have been born after approximately 1,500 PGD cycles for single gene disorders (ESHRE PGD Consortium Steering Committee 2000; Harper 2003). The technique involves the use of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology on a single cell and subsequent analysis by either conventional or advanced molecular genetics tools as DNA sequencing. Although, the first successful PGD application was based on sex selection for X-linked disorders, as the accuracy and the technical ease is improving, many autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive and X-linked genetic disorders, can now be diagnosed on preimplantation embryos by using one or two blastomeres obtained after embryo biopsy (Table I) (Handyside et al., 1990; Sermon 2002; Verlinsky and Kuliev 2002).
PGD for single gene disorders is further expanded to cancer predisposition, late onset disorders, or even serves as a therapeutic option for an affected sibling by preimplantation HLA typing (Verlinsky et al., 2001; Rechitsky et al., 2002, 2003). The latter is of importance, since it gives the unique opportunity for families in which an HLA compatible sibling can be born and its cord blood or bone marrow stem cells can be the ideal source for transplantation, leading to a successful restoration of the affected phenotype. Although the number of cases are currently limited to draw a general conclusion, reported results on 25 pregnancies obtained after 147 preimplantation HLA typing cycles are highly encouraging. However, certain clinical and patient specific factors can limit the successful pregnancy outcome. (Van de Velde et al., 2004; Fiorentino et al., 2004; Kuliev and Verlinsky, 2004b; Rechitsky et al., 2004; Kahraman et al., 2004c)
Besides its demonstrated diagnostic and therapeutic value, strict precautions should be taken, since several problems such as external contamination, allelic drop-out or preferential amplification effect the results and the reliability of the technique. Nowadays, designing sterile and dedicated area with special labware, apparatus and technical improvements such as the intruduction of nested and multiplex PCR systems seem to minimize these problems (Findlay et al., 1998; Lewis et al., 2001; Fiorentino et al., 2003).

Methodology and technical approaches
There are mainly two embryo development stages that sampling for PGD can be done: MII oocyte or prezygote stage and cleavage stage (Figure 1). First and second polar bodies of either an oocyte or fertilized zygote can be analyzed for a given chromosomal or DNA-sequence-based genetic defect. However, results obtained constitute only the maternal profile and do not give information regarding paternal contribution. On the other hand blastomere biopsy, reveals genetic information that is inherited from both parents. Advantages and disadvantages of these sampling stages on the analysis outcome are summarized in Table II.
Polar bodies are the by-products of the first and second meiotic divisions which appear after maturation of oocyte or fertilization. This type of analysis is usually preferred for the maternal indications which bring high aneuploidy risk in oocytes such as advanced maternal age and translocations in which female is the carrier. For other indications such as recurrent abortions, recurrent implantation failure and severe male infertility etc., evaluation of the blastomere is needed. In this case, biopsy is done by removing one or two blastomeres from a cleavage-stage embryo having 6-8 cells. Some centers use both polar body and blastoemere biopsy in order to increase the accuracy of the results (Kuliev et al., 2002). Also, biopsy can also be done at the blastocyst stage, involving the removal of multiple trophectoderm cells. Although the clinical data regarding the results are limited.
In all three stages, a partial opening on the zona pellucida should be created by either mechanical, chemical or laser-driven systems. A recent study compared the clinical outcome after different methods of zona opening and found insignificant differences of one technique to another (Joris et al., 2003). Therefore, subsequent aspiration of either polar bodies or a blastomere after zona opening is performed and obtained material is processed for either FISH (Figure 2) or single cell PCR. It has also been reported that, when compaction is observed during blastomere biopsy, short-term incubation of the embryo in Ca-Mg free media helps to facilitate the procedure (Kahraman et al., 2000). In order to study chromosomal abnormalities by FISH, biopsied samples are first fixed on a slide and subsequently analyzed after hybridization with probes specific for chromosomes to be analyzed. Several fixation methods are now available and their advantages and possible drawbacks such as the risk of misdiagnosis have recently been evaluated (Velila et al., 2002).



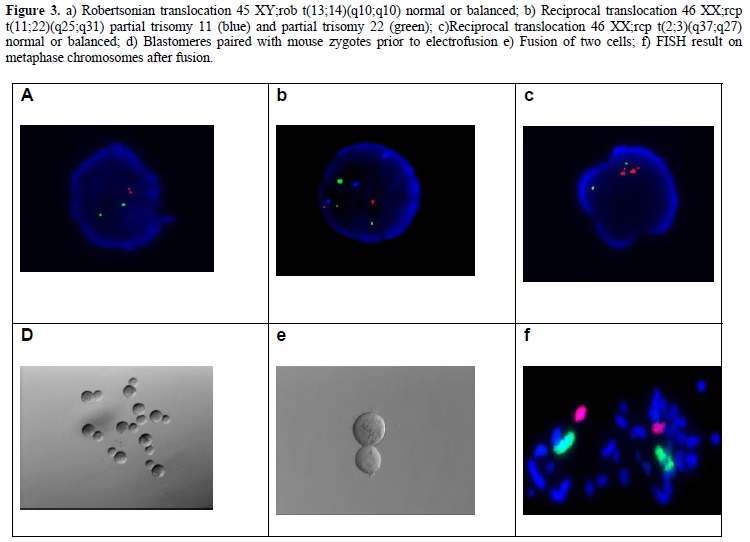
Current limitations and future prospectives
Although, the application of PGD becomes an invaluable tool for ART and clinical genetics, in order to increase its efficiency, several limitations should be overcomed. First, the fact that only a limited subset of chromosomes can be analyzed in conventional FISH techniques restricts the successful outcome in PGD-AS applications (Munne and Weier 1996; Munne et al., 1999). This limitation is mainly attributed as technical, since it involves chromosome analysis on interphase nucleus, other than metaphase spreads which could allow karyotyping hence making the analysis of all the chromosomes possible. Interphase FISH also fails to determine whether the analyzed arrangement is normal or balanced in the case of structural chromosomal abnormalities. However, it has recently been reported that the application of nucleus conversion technique, which involves the fusion of a biopsied sample with a bovine or a mouse zygote successfuly converted the interphase nucleus to a metaphase plate, giving reproducible and efficient results that can be analyzed for PGD (Evsikov and Verlinsky 1999; Willadsen et al., 1999). Representative images of this technique are shown in Figure 3. Application of this technique has recently been shown to be applied on 94 cycles, giving a 30.3% pregnancy rate (Verlinsky 2002).
Likewise, comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) has also been proposed as an alternative to interphase FISH. However, the time required (2-3 days) for the analysis requires cleavage stage embryos to be cryopreserved hence is not suitable for current clinical procedures. Although, successful pregnancies have been reported by CGH, cryopreservation after biopsy gives lower viability and poor ART outcome (Joris et al., 1999; Magli et al., 1999; Wilton et al., 2001; 2002). In the near future, improvements in the protocols, either shortening the time required for CGH or cryopreservation will create an alternative protocol for analyzing the whole set of chromosomes in a given embryo.
Another approach, which utilizes PCR and sequencing-based methods hence named as DNA fingerprinting has been developed and tested for the most common chromosomal abnormalities such as trisomy 21 (Katz et al., 2003). This technique initially included markers for 5 chromosomes. However, it needs to be determined whether this number can be sufficiently increased and be a powerful alternative to conventional FISH analysis. Recent developments in microarray technology have been another powerful tool in reproductive medicine. Although, the first impact would be the analysis of gene expression or mutation profiles on oocytes and embryos of different developmental stages which can provide potential targets for diagnosis. Development of customized microarrays, in which aneuploidy testing for all chromosomes could be possible, would boost the efficiency and eliminate the use of conventional FISH techniques. Several microarray prototypes have already been designed for standard aneuploidy testing and for Robertsonian translocations; however, the technique requires further clinical confirmations and improvements (Kuliev and Verlinsky 2004a).
Although, the successful results are obtained in more than 90% of the blastomeres analyzed during conventional FISH analysis, the presence of mosaicism is of a major concern in PGD-AS cycles. It has been reported that a certain rate of mosaicism is present in preimplantation embryos and this rate is even higher in certain cases such as patients with severe sperm defects and advanced maternal age. (Magli et al., 2000; Bialenska et al., 2002; Munne et al., 2002; Sherman et al., 2003;). Obtained results can therefore carry a risk of representing false results, that is an embryo with majority of chromosomally normal blastomeres can be diagnosed as aneuploid and discarded from embryo transfer procedure.
Conclusion
In summary, cumulative analysis of more than 6000 PGD cycles performed to date indicates that application of PGD (i) prevents genetic disorders in couples at risk of having a child with a genetic disease, (ii) reduces the risk of high order pregnancies as well as repeated early abortions especially for translocation carrier couples and (iii) improves the ART outcome in poor prognosis patients such as women with increased maternal age. Expanding indications as well as novel approaches such as preimplantation HLA typing and the application of DNA microarray technologies also make PGD not only a diagnostic, but also a therapeutic tool for ART clinics. Although, there exist some limitations to be overcomed with technical protocols, results of the accumulated clinical data is encouraging and the validity as well as accuracy have already been proven. Therefore, PGD facilities have already become an integrated part of an increased number of ART clinics worldwide.
It has been reported that nearly 50% of the cases with early pregnancy loss contain chromosomal abnormalities (Chandley 1984; Zenzes and Casper 1992; Jacobs ve Hassold 1995; Jobanputra et al., 2002). Although most of them are found to be eliminated before implantation, some anomalies such as trisomies of chromosomes 13, 18 and 21 can reach to blastocyst stage and even result in affected offspring (Sandalinas et al., 2001). Chromosomal aneuploidy has also been shown to increase under inappropriate stimulation protocols, suboptimal culture conditions, paternal factors and lack of certain growth factors (Munne et al., 1995; Janny and Menezo 1996; Kaye 1997; Moor et al., 1998; Calogero et al., 2003; Findikli et al., 2004).
Screening preimplantation embryos for certain chromosomal abnormalities is generally termed as PGD for aneupoloidy screening (PGD-AS). It is based on the principle that detection and elimination of chromosomally abnormal embryos before embryo transfer could increase the reproductive efficiency in certain cases where aneuploidy is proven or likely to exert a negative effect (Munne et al., 1995; Benadiva et al., 1996; Kuliev et al., 2002). So far, applications of PGD for aneuploidy screening to a large extent involved indications such as advanced maternal age, repeated implantation failures and recurrent abortion (Munne et al., 1999; Gianaroli et al., 2001; Kuliev et al., 2002; Munne 2002; Wilton 2002; Pehlivan et al., 2003; Rubio et al., 2003; Kahraman et al., 2004a). Due to their increased risk of producing aneuploid gamete cells, carriers of structural abnormalities such as inversions and translocations are also among other PGD candidates.
Improved clinical outcome with decreased early abortions after selection of abnormal embryos with PGD have recently been reported by different groups on reciprocal and Robertsonian translocations (Conn et al., 1998; Scriven et al., 1998, 2000; Munne et al., 1998, 2000; Findikli et al., 2003). Furthermore, the positive effect of PGD application on clinical results was recently documented in severe male infertility, Klinefelter’s syndrome and cases with abnormal gamete cell morphology, which are among other potential PGD indications (Gianaroli et al., 2001; Kahraman et al., 2000; 2003, 2004a, 2004b; Aran et al., 2004;). The data accumulated on approximately 5000 PGD cycles having above indications clearly shows that the prevalence of chromosomal abnormalities in oocytes as well as at cleavage stages can be as high as 50-70%. Elimination of such embryos prevents the birth of a trisomic child, decreases the abortion as well as high order pregnancy rates and has a positive impact on implantation, validating the beneficial approach of selecting euploid embryos for embryo transfer in PGD for certain indications (IWGPG 2001; Munne et al., 2003; Kuliev and Verlinsky 2004a).
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis for single gene disorders
If one or both partners are carriers of a genetic disease, in order to prevent the birth of an affected offspring, preimplantation embryos can be screened for a known genetic defect. Up to date, more than 300 healthy children have been born after approximately 1,500 PGD cycles for single gene disorders (ESHRE PGD Consortium Steering Committee 2000; Harper 2003). The technique involves the use of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology on a single cell and subsequent analysis by either conventional or advanced molecular genetics tools as DNA sequencing. Although, the first successful PGD application was based on sex selection for X-linked disorders, as the accuracy and the technical ease is improving, many autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive and X-linked genetic disorders, can now be diagnosed on preimplantation embryos by using one or two blastomeres obtained after embryo biopsy (Table I) (Handyside et al., 1990; Sermon 2002; Verlinsky and Kuliev 2002).
PGD for single gene disorders is further expanded to cancer predisposition, late onset disorders, or even serves as a therapeutic option for an affected sibling by preimplantation HLA typing (Verlinsky et al., 2001; Rechitsky et al., 2002, 2003). The latter is of importance, since it gives the unique opportunity for families in which an HLA compatible sibling can be born and its cord blood or bone marrow stem cells can be the ideal source for transplantation, leading to a successful restoration of the affected phenotype. Although the number of cases are currently limited to draw a general conclusion, reported results on 25 pregnancies obtained after 147 preimplantation HLA typing cycles are highly encouraging. However, certain clinical and patient specific factors can limit the successful pregnancy outcome. (Van de Velde et al., 2004; Fiorentino et al., 2004; Kuliev and Verlinsky, 2004b; Rechitsky et al., 2004; Kahraman et al., 2004c)
Besides its demonstrated diagnostic and therapeutic value, strict precautions should be taken, since several problems such as external contamination, allelic drop-out or preferential amplification effect the results and the reliability of the technique. Nowadays, designing sterile and dedicated area with special labware, apparatus and technical improvements such as the intruduction of nested and multiplex PCR systems seem to minimize these problems (Findlay et al., 1998; Lewis et al., 2001; Fiorentino et al., 2003).

Methodology and technical approaches
There are mainly two embryo development stages that sampling for PGD can be done: MII oocyte or prezygote stage and cleavage stage (Figure 1). First and second polar bodies of either an oocyte or fertilized zygote can be analyzed for a given chromosomal or DNA-sequence-based genetic defect. However, results obtained constitute only the maternal profile and do not give information regarding paternal contribution. On the other hand blastomere biopsy, reveals genetic information that is inherited from both parents. Advantages and disadvantages of these sampling stages on the analysis outcome are summarized in Table II.
Polar bodies are the by-products of the first and second meiotic divisions which appear after maturation of oocyte or fertilization. This type of analysis is usually preferred for the maternal indications which bring high aneuploidy risk in oocytes such as advanced maternal age and translocations in which female is the carrier. For other indications such as recurrent abortions, recurrent implantation failure and severe male infertility etc., evaluation of the blastomere is needed. In this case, biopsy is done by removing one or two blastomeres from a cleavage-stage embryo having 6-8 cells. Some centers use both polar body and blastoemere biopsy in order to increase the accuracy of the results (Kuliev et al., 2002). Also, biopsy can also be done at the blastocyst stage, involving the removal of multiple trophectoderm cells. Although the clinical data regarding the results are limited.
In all three stages, a partial opening on the zona pellucida should be created by either mechanical, chemical or laser-driven systems. A recent study compared the clinical outcome after different methods of zona opening and found insignificant differences of one technique to another (Joris et al., 2003). Therefore, subsequent aspiration of either polar bodies or a blastomere after zona opening is performed and obtained material is processed for either FISH (Figure 2) or single cell PCR. It has also been reported that, when compaction is observed during blastomere biopsy, short-term incubation of the embryo in Ca-Mg free media helps to facilitate the procedure (Kahraman et al., 2000). In order to study chromosomal abnormalities by FISH, biopsied samples are first fixed on a slide and subsequently analyzed after hybridization with probes specific for chromosomes to be analyzed. Several fixation methods are now available and their advantages and possible drawbacks such as the risk of misdiagnosis have recently been evaluated (Velila et al., 2002).




Current limitations and future prospectives
Although, the application of PGD becomes an invaluable tool for ART and clinical genetics, in order to increase its efficiency, several limitations should be overcomed. First, the fact that only a limited subset of chromosomes can be analyzed in conventional FISH techniques restricts the successful outcome in PGD-AS applications (Munne and Weier 1996; Munne et al., 1999). This limitation is mainly attributed as technical, since it involves chromosome analysis on interphase nucleus, other than metaphase spreads which could allow karyotyping hence making the analysis of all the chromosomes possible. Interphase FISH also fails to determine whether the analyzed arrangement is normal or balanced in the case of structural chromosomal abnormalities. However, it has recently been reported that the application of nucleus conversion technique, which involves the fusion of a biopsied sample with a bovine or a mouse zygote successfuly converted the interphase nucleus to a metaphase plate, giving reproducible and efficient results that can be analyzed for PGD (Evsikov and Verlinsky 1999; Willadsen et al., 1999). Representative images of this technique are shown in Figure 3. Application of this technique has recently been shown to be applied on 94 cycles, giving a 30.3% pregnancy rate (Verlinsky 2002).
Likewise, comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) has also been proposed as an alternative to interphase FISH. However, the time required (2-3 days) for the analysis requires cleavage stage embryos to be cryopreserved hence is not suitable for current clinical procedures. Although, successful pregnancies have been reported by CGH, cryopreservation after biopsy gives lower viability and poor ART outcome (Joris et al., 1999; Magli et al., 1999; Wilton et al., 2001; 2002). In the near future, improvements in the protocols, either shortening the time required for CGH or cryopreservation will create an alternative protocol for analyzing the whole set of chromosomes in a given embryo.
Another approach, which utilizes PCR and sequencing-based methods hence named as DNA fingerprinting has been developed and tested for the most common chromosomal abnormalities such as trisomy 21 (Katz et al., 2003). This technique initially included markers for 5 chromosomes. However, it needs to be determined whether this number can be sufficiently increased and be a powerful alternative to conventional FISH analysis. Recent developments in microarray technology have been another powerful tool in reproductive medicine. Although, the first impact would be the analysis of gene expression or mutation profiles on oocytes and embryos of different developmental stages which can provide potential targets for diagnosis. Development of customized microarrays, in which aneuploidy testing for all chromosomes could be possible, would boost the efficiency and eliminate the use of conventional FISH techniques. Several microarray prototypes have already been designed for standard aneuploidy testing and for Robertsonian translocations; however, the technique requires further clinical confirmations and improvements (Kuliev and Verlinsky 2004a).
Although, the successful results are obtained in more than 90% of the blastomeres analyzed during conventional FISH analysis, the presence of mosaicism is of a major concern in PGD-AS cycles. It has been reported that a certain rate of mosaicism is present in preimplantation embryos and this rate is even higher in certain cases such as patients with severe sperm defects and advanced maternal age. (Magli et al., 2000; Bialenska et al., 2002; Munne et al., 2002; Sherman et al., 2003;). Obtained results can therefore carry a risk of representing false results, that is an embryo with majority of chromosomally normal blastomeres can be diagnosed as aneuploid and discarded from embryo transfer procedure.
Conclusion
In summary, cumulative analysis of more than 6000 PGD cycles performed to date indicates that application of PGD (i) prevents genetic disorders in couples at risk of having a child with a genetic disease, (ii) reduces the risk of high order pregnancies as well as repeated early abortions especially for translocation carrier couples and (iii) improves the ART outcome in poor prognosis patients such as women with increased maternal age. Expanding indications as well as novel approaches such as preimplantation HLA typing and the application of DNA microarray technologies also make PGD not only a diagnostic, but also a therapeutic tool for ART clinics. Although, there exist some limitations to be overcomed with technical protocols, results of the accumulated clinical data is encouraging and the validity as well as accuracy have already been proven. Therefore, PGD facilities have already become an integrated part of an increased number of ART clinics worldwide.
Type of Study: Original Article |
References
1. Aran B., Veiga A., Vidal F., Parriego M., Vendrell J.M., Santalo J., Egozcue J., and Barri P.N. (2004) Preimplantation genetic diagnosis in patients with male meiotic abnormalities. RBM Online 8: 470-476. [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)60932-7]
2. Benadiva C.A., Kligman I., and Munné J.S. (1996) Aneuploidy 16 in human embryos increases significantly with maternal age. Fertil Steril 66:248-255. [DOI:10.1016/S0015-0282(16)58448-9]
3. Bielanska M., Tan L.S., and Ao A. (2002) Chromosomal mosaicism throughout human preimplantation development in vitro: incidence, type, and relevance to embryo outcome. Human Reproduction 2: 413-419. [DOI:10.1093/humrep/17.2.413] [PMID]
4. Calogero A., Burello N., De Palma A., Barone N., D'Agata R., and Vicari E. (2003) Sperm aneuploidy in infertile men. Reprod BioMed Online 6:310-317. [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)61850-0]
5. Chandley A.C. (1984) Infertility and chromosomal abnormality. Oxford Rev Reprod Biol. 6:1-46.
6. Conn C.M., Harper J.C., Winston R.M., and Delhanty J.D. (1998) Infertile couples with Robertsonian translocations: preimplantation genetic analysis of embryos reveals chaotic cleavage divisions. Hum Genet 102:117-123. [DOI:10.1007/s004390050663] [PMID]
7. Eksikov S., and Verlinsky Y. (1999) Visualization of chromosomes in single human blastomeres. J Assis Reprod Genet 16:133-137. [DOI:10.1023/A:1022579731014] [PMID] [PMCID]
8. ESHRE PGD Consortium Steering Committee: (2000) ESHRE Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) Consortium: data collection II. Hum Reprod 15:2673-2683. [DOI:10.1093/humrep/15.12.2673] [PMID]
9. Findikli N., Kahraman S., Kumtepe Y., Donmez E., Biricik A., Sertyel S., Berkil H., and Melil S. (2003) Embryo development characteristics in Robertsonian and reciprocal translocations: a comparison of the results with non-translocation cases. RBM Online 7(5): 563-571. [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)62073-1]
10. Findikli N., Kahraman S., ,Kumtepe Y., Donmez E., Benkhalifa M., Biricik A., Sertyel S., Berkil H., and Oncu N. (2004) Assessment of DNA fragmentation and aneupoloidy on poor quality human embryos. RBM Online 8(2): 196-206. [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)60516-0]
11. Findlay I., Matthews P., and Quirke P. (1998) Multiple genetic diagnosis from single cells using multiplex PCR: reliability and allele drop-out. Prenat Diagn, 18:1413-1421.
https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0223(199812)18:13<1413::AID-PD496>3.0.CO;2-1 [DOI:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0223(199812)18:133.0.CO;2-1]
12. Fiorentino F., Magli M.C., Podini D., Ferraretti A.P., Nuccitelli A., Vitale N., Baldi M., and Gianaroli L. (2003) The minisequencing method: An alternative strategy for preimplantation genetic diagnosis for single gene disorders. Molecul Hum Reprod 9: 399-410. [DOI:10.1093/molehr/gag046] [PMID]
13. Fiorentino F., Biricik A., Karadayi H., Berkil H., Karlikaya G., Sertyel S., Podini D., Baldi M., Magli M.C., Gianaroli L., and Kahraman S. (2004) Development and clinical application of a strategy for preimplantation genetic diagnosis of single gene disorders combined with HLA matching. Molecul Hum Reprod 9: 399-410. [DOI:10.1093/molehr/gag046] [PMID]
14. Gianaroli L., Magli C.M., Ferraretti A.P., Tabanelli C., Trombetta C., and Boudjema E. (2001) The role of preimplantation diagnosis for aneuploidies. RBM Online 4: 31-36. [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(12)60113-8]
15. Handyside A.H., Kontogianni E.H., Hardy K., and Winston R.M. (1990) Pregnancies from biopsied human preimplantation embryos sexed by Y-specific DNA amplification. Nature 344: 768-770. [DOI:10.1038/344768a0] [PMID]
16. Harper J. (2003) ESHRE PGD Consotium experience for Mendelian disorders (Abstract) Fifth International Symposium on Preimplantation Genetics, 18.
17. International Working Group on Preimplantation Genetics. (2001) 10th Anniversary of Preimplantation genetic Diagnosis. Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics 18:66-72.
18. Jacobs P.A., and Hassold T.J. (1995) The origin of numerical chromosomal abnormalities. Advances in Genetics 33: 101-133. [DOI:10.1016/S0065-2660(08)60332-6]
19. Janny L., and Menezo Y.J. (1996) Evedence for a strong paternal effect on human preimplantation embryo development and blastocyst formation. Molecular Reproduction and Development 38: 36-42. [DOI:10.1002/mrd.1080380107] [PMID]
20. Jobanputra V., Sobrino A., Kinney A., Kline J., and Warburton D. (2002) Multiplex interphase FISH as ascreen for common aneuploidies in spontaneous abortions. Hum Reprod 17: 1166-1170. [DOI:10.1093/humrep/17.5.1166] [PMID]
21. Joris H., Van Der Abbeel E., Vos A.D., and Van Steirteghem A. (1999) Reduced survival after human embryo biopsy and subsequent cryopreservation. Hum Reprod 14: 2833-2837. [DOI:10.1093/humrep/14.11.2833] [PMID]
22. Joris H., Vos A.D., Janssens R., Devroey P., Liebaers I., and Van Steirteghem A. (2003) Comparison of the results of human embryo biopsy and outcome of PGD after zona drilling using acid Tyrode medium or a laser. Hum Reprod 18: 1896-1902. [DOI:10.1093/humrep/deg355] [PMID]
23. Kahraman S., Bahce M., Samli H., Imirzalioglu N., Yakisn K., Cengiz G., and Donmez E. (2000) Healthy births and ongoing pregnancies obtained by preimplantation genetic diagnosis in patients with advanced maternal age and recurrent implantation failure. Hum Reprod 15:2003-2007. [DOI:10.1093/humrep/15.9.2003] [PMID]
24. Kahraman S., Findikli N., Berkil H., Bakircioglu E., Donmez E., Sertyel S., and Biricik A. (2003) Results of preimplantation genetic diagnosis in patients with klinefelter's syndrome. RBM Online 7:346-352. [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)61876-7]
25. Kahraman S., Benkhalifa M., Donmez E., Biricik A., Sertyel S., Findikli N., and Berkil H. (2004a) The results of aneuploidy screening in 276 couples undergoing assisted reproductive techniques. Prenatal Diagnosis 4:307-311. [DOI:10.1002/pd.842] [PMID]
26. Kahraman S., Sertyel S., Findikli N., Kumtepe Y., Oncu N., Melil S., Unal S., Yelke H., and Vanderzwalmen P. (2004b) The effect of PGD on implantation and ongoing pregnancy rates in cases with dominantly macrocephalic sperm samples. RBM Online 9:79-85. [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)62114-1]
27. Kahraman S., Karlikaya G., Sertyel S., Karadayi H., Findikli N., Oncu O., Biricik A., and Fiorentino F. (2004c) Clinical Aspects of Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis for Single Gene Disorders Combined with HLA Typing. RBM Online (submitted). [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)61637-9]
28. Katz M., Mansfield J., Gras L., Trounson A.O., and Cram D.S. (2002) Diagnosis of trisomy 21 in preimplantation embryos by single- cell DNA fingerprinting. RBM Online 4: 43-50. [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)61914-1]
29. Kaye P.L. (1997) Preimplantation growth factor physiology. Reviews of Reproduction 2: 121-127. [DOI:10.1530/ror.0.0020121] [PMID]
30. Kuliev A., Cieslak C., Illmevitch Y., and Verlinsky Y. (2002) Chromosomal abnormalities in a series of 6733 human oocytes in preimplantation diagnosis for age-related aneuploidies. RBM Online 6:54-59. [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)62055-X]
31. Kuliev A., and Verlinsky Y. (2004a) Thirteen years' experience of preimplantation diagnosis: report of the Fifth International Symposium on Preimplantation Genetics. RBM Online 8: 229-235. [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)60521-4]
32. Kuliev A., and Verlinsky Y. (2004b). Preimplantation HLA typing and stem cell transplantation: report of International Meeting, Cyprus 27-28 March 2004. RBM Online (accepted for publication). [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)62131-1]
33. Lewis C.M., Pinel T., Whittaker J.C., and Handyside A.H. (2001) Controlling misdiagnosis errors in preimplantation genetic diagnosis: a comprehensive model encompassing extrinsic and intrinsic sources of error. Hum Reprod 16: 43-50. [DOI:10.1093/humrep/16.1.43] [PMID]
34. Magli C.M., Gianaroli L., Fortini D., Ferraretti A.P., and Munne S. (1999) Impact on blastomere biopsy and cryopreservation techniques on human embryo viability. Hum Reprod 14: 770-773. [DOI:10.1093/humrep/14.3.770] [PMID]
35. Magli M.C., Jones G.M., Gras L., Gianaroli L., Korman I., and Trounson A.O. (2000) Chromosome mosaicism in day 3 aneuploid embryos that develop to morphologically normal blastocysts in vitro. Hum Reprod 15: 1781-1786. [DOI:10.1093/humrep/15.8.1781] [PMID]
36. Moor R.M., Dai Y., Lee C., and Fulka J. (1998) Oocyte maturation and embryonic failure. Hum Reprod Update 4: 223-236. [DOI:10.1093/humupd/4.3.223] [PMID]
37. Munné J.S., Morrison L., Fung J., Marquez C., Weier U., Bahce M., Sable D., Grunfeld L., Schoolcraft B., Scott R., and Cohen J. (1998) Spontaneous abortions are reduced after preconception diagnosis of translocations. J of Assis Reprod and Genet 15:290-296. [DOI:10.1023/A:1022544511198] [PMID] [PMCID]
38. Munné J.S., Magli C., Cohen J., Morton P., Sadowy S., Gianaroli L., Tucker M., Marquez C., Sable D., Ferraretti A.P., Massey J.B., and Scott R. (1999) Positive outcome after preimplantation diagnosis of aneuploidy in human embryos. Hum Reprod 14:2191-2199. [DOI:10.1093/humrep/14.9.2191] [PMID]
39. Munné J.S., Sandalinas M., Escudero T., Fung J., Gianaroli L., and Cohen J. (2000) Outcome of preimplantation genetic diagnosis of translocations. Fertil Steril 73:1209-1218. [DOI:10.1016/S0015-0282(00)00495-7]
40. Munne S., Alikani M., Tomkin G., Grifo J., and Cohen J. (1995) Embryo morphology, developmental rates, and maternal age are correlated with chromosome abnormalities. FertilSteril 64: 382-391. [DOI:10.1016/S0015-0282(16)57739-5]
41. Munne S., and Weier H.U. (1996) Simultaneous enumeration of chromosomes 13, 18, 21, X and Y in interphase cells for preimplantation genetic diagnosis for aneuploidy. Cytogenet Cell Genet 75: 263-270. [DOI:10.1159/000134497] [PMID]
42. Munne S. (2002) Preimplantation genetic diagnosis of numerical and structural chromosome abnormalities RBM Online 4: 183-196. [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)61938-4]
43. Munne S., Sandalinas M., Escudero T., Marquez C., and Cohen J. (2002) Chromsome mosaicism in cleavage-stage human embryos: evidence of a maternal age effect. RBM Online 4: 223-232. [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)61810-X]
44. Munne S., Sandalinas M., Escudero T., Velila E., Walmsley R., Sadowy S., Cohen J., and Sable D. (2003) Improved implantation after preimplantation genetic diagnosis for aneuploidy. RBM Online 7:91-97. [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)61735-X]
45. Pehlivan T., Rubio C., Rodrigo L., Romero J., Remohi J., Simon C., and Pellicer A. (2003) Impact of preimplantation genetic diagnosis on IVF outcome in implantation failure patients. RBM Online 6: 232-237. [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)61715-4]
46. Rechitsky S., Verlinsky O., Cristokhina A., Sharapova T., Ozen S., Masciangelo C., Kuliev A., and Verlinsky Y. (2002) Preimplantation genetic diagnosis for cancer predisposition. RBM Online 5:148-155. [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)61617-3]
47. Rechitsky S., Verlinsky O., Masciangelo C., Tur-Kaspa I., Kuliev A., and Verlinsky Y. (2003) Preimplantation non-disease testing (Abstract). Fifth International Symposium on Preimplantation Genetics, 17.
48. Rechitsky S., Tur-Kaspa I., Kuliev A., and Verlinsky Y. (2004) Preimplantation genetic diagnosis with HLA Matching. RBM Online (accepted for publication) [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)62132-3]
49. Rubio C., Simon C., Vidal F., Rodrigo L., Pehlivan T., Remohi J., and Pellicer A. (2003) Chromosome abnormalities and embryo development in recurrent miscarriage couples. Hum Reprod 18: 182-188. [DOI:10.1093/humrep/deg015] [PMID]
50. Sandalinas M., Sadowy S., Alikani M., Calderon G., Cohen J., and Munne S. (2001) Developmental ability of chromosomally abnormal human embryos to develop to the blastocyst stage. Hum Reprod 16: 1954-1958. [DOI:10.1093/humrep/16.9.1954] [PMID]
51. Scriven P.N., Handyside A.H., and Ogilvie C. (1998) Chromosome translocations: segregation modes and strategies for preimplantation genetic diagnosis. Prenatal Diagnosis 18:1437-1549.
https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0223(199812)18:13<1437::AID-PD497>3.0.CO;2-P [DOI:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0223(199812)18:133.0.CO;2-P]
52. Scriven PN. (2000) Clinical pregnancy following blastomere biopsy and PGD for a reciprocal translocation carrier: analysis of meiotic outcomes and embryo quality in two IVF cycles. Prenatal Diagnosis 20:587-592.
https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0223(200007)20:7<587::AID-PD873>3.0.CO;2-W [DOI:10.1002/1097-0223(200007)20:73.0.CO;2-W]
53. Sermon K. (2002) Current concepts in preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD): a molecular biologist's view. Hum Reprod Update 8: 11-20. [DOI:10.1093/humupd/8.1.11] [PMID]
54. Silber S., Escudero T., Lenahan K., Abdelhadi I., Kilani Z., and Munne S. (2003) Chromosomal abnormalities in embryos derived from testicular sperm extraction Fertil Steril 79: 30-38. [DOI:10.1016/S0015-0282(02)04407-2]
55. Van de Velde H., Georgiou I., De Rycke M., Schots R., Sermon K., Lissens W., Devroey P., and Van Steirteghem, Liebaers I. (2004) Novel universal approach for preimplantation genetic diagnosis of -thalassaemia in combination with HLA matching of embryos. Hum Reprod 19: 700-708. [DOI:10.1093/humrep/deh153] [PMID]
56. Velila E., Escudero T., and Munne S. (2002) Blastomere fixation techniques and risk of misdiagnosis for preimplantation genetic diagnosis of aneuploidy. RBM Online 4: 210-217. [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)61808-1]
57. Verlinksy Y., and Kuliev A. (2002) Current Status of preimplantation diagnosis for single gene disorders. RBM Online 7: 145-150. [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)61744-0]
58. Verlinsky Y., Rechitsky S.., Schoolcraft W., Strom C., and Kuliev A. (2001) Preimplantation Diagnosis for Fanconi Anemia Combined with HLA Matching. JAMA 285: 3130-3133. [DOI:10.1001/jama.285.24.3130] [PMID]
59. Verlinsky Y. (2002) Nuclear transfer for full karyotyping and preimplantation diagnosis for translocations. RBM Online 3: 300-305. [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)61836-6]
60. Willadsen S., Levron J., Munné S., Schimmel T., Marquez C., Scott R., and Cohen J. (1999) Rapid visualization of metaphase chromosomes in single human blastomeres after fusion with in-vitro matured bovine eggs. Hum Reprod 14:470-475. [DOI:10.1093/humrep/14.2.470] [PMID]
61. Wilton L., Williamson R., McBain J., Edgar D., and Voulaire L. (2001) Birth of a healthy infant after preimplantation confirmation of euploidy by comparative genomic hybridization. New England J of Med 345: 1537-1541. [DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa011052] [PMID]
62. Wilton L. (2002) Preimplantation genetic diagnosis for aneuploidy screening in early human embryos: a review. Prenatal Diagnosis 22: 512-518. [DOI:10.1002/pd.388] [PMID]
63. Wilton L., Williamson R., McBain J., Edgar D., and Voulaire L. (2002) Preimplantation of aneuploidy using comparative genomic hybridization RBM Online 4: 13. [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(12)60029-7]
64. Zenzes M.T., and Casper R.F. (1992) Cytogenetics of human oocytes, zygotes and embryos after in vitro fertilization. Hum Genet 88:367-375. [DOI:10.1007/BF00215667] [PMID]
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |




