Sun, Jul 13, 2025
[Archive]
Volume 18, Issue 7 (July 2020)
IJRM 2020, 18(7): 485-490 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Aflatoonian A, Haghighi F, Hoseini M, Haghdani S. Does the repeat dose of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist trigger in polycystic ovarian syndrome improve in vitro fertilization cycles outcome? A clinical trial study. IJRM 2020; 18 (7) :485-490
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-1662-en.html
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-1662-en.html
1- Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Research and Clinical Center for Infertility, Yazd Reproductive Sciences Institute, Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Science, Yazd, Iran.
2- Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Research and Clinical Center for Infertility, Yazd Reproductive Sciences Institute, Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Science, Yazd, Iran. ,dr.haghighi120832@gmail.com
3- Department of Urology, Hasheminejad Kidney Research Center (HKRC), Iran University of Medical Science, Tehran, Iran.
2- Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Research and Clinical Center for Infertility, Yazd Reproductive Sciences Institute, Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Science, Yazd, Iran. ,
3- Department of Urology, Hasheminejad Kidney Research Center (HKRC), Iran University of Medical Science, Tehran, Iran.
Keywords: Polycystic ovarian syndrome, Treatment, In vitro fertilization, Gonadotropin-Releasing hormone.
Full-Text [PDF 311 kb]
(1473 Downloads)
| Abstract (HTML) (2487 Views)
In addition, in PCOS women and hyper responders after GnRHa trigger, the gonadotropin answer is greatly shorter than endogenic LH surge in a natural cycle that causes more suboptimal expected answer (12, 13). The underlying mechanisms proposed are that some women with PCOS show neuro-endocrine abnormalities; moreover, the supraphysiologic estradiol (E2) level cause apparent increase in the number of follicles and insufficient number of LH receptor (14), therefore, a single dose of GnRHa might not lead to LH surge over a threshold level in these participants. In order to gain optimum responses, repeated dose 12 hr after starting doses of GnRHa resulted in terms of better maturity of oocytes, higher number of blastocysts, and higher clinical pregnancy in Deepikaand colleagues study. In a similar research, we aimed to evaluate if a second dose 12 hr. after the first dose of GnRH agonist trigger could provide long duration of LH surge and amplitude appropriately making an improvement in oocyte maturity.
The aim of this study was to see weather oocyte maturity will improve by a repeat dose of GnRHa or not?
The inclusion criteria were 1) PCOS women outlined based on ESHRE ASRM Rotterdam criteria, 2) stimulation in a GnRH ant protocol, 3) age 20-38 yr, 4) E2 concentration > 3000 IU on trigger day, 5) Body Mass Index > 18 and < 30, 6) indication for IVF, and 7) participants’ desire
The exclusion criteria were 1) severe male factor, 2) uterine abnormally, 3) endometriosis, and 4) metabolic disease (ex. Diabetes).
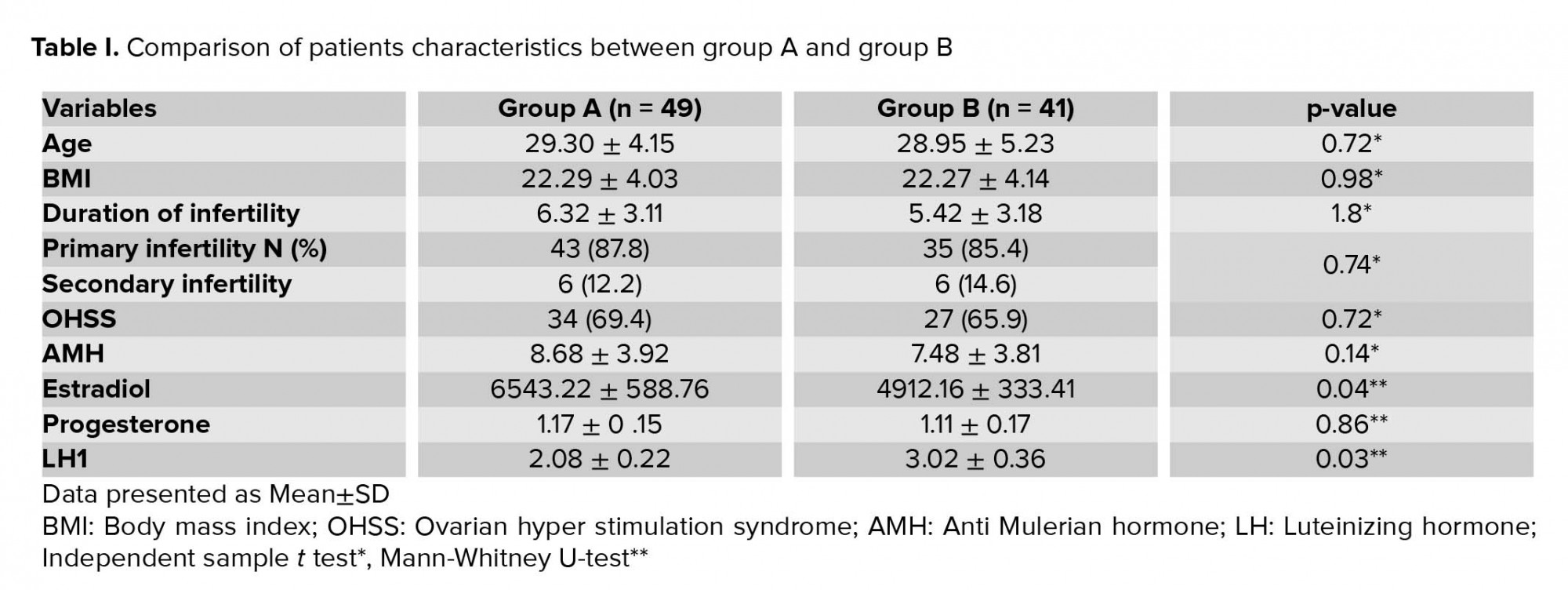
Serum E2, LH, and progesterone concentration were measured on the trigger day when three lead follicles reached 17 mm in diameter. Participants with serum E2 > 3000 based on randomization table number were divided in two groups. Final oocyte maturation was triggered with a single dose of 0.2 mg sc triptorelin (decapeptyl) 34-36 hr. prior to oocyte retrieval in both groups. In group A, a repeat dose of 0.1 mg, 12 hr after the first dose was prescribed, but in group B, a single dose of GnRHa 0.2 mg sc triptorelin (decapeptyl) was given. In group A, serum LH was measured 12 hr. after the first dose of GnRHa administration, and then again after the second dose of GnRHa and prior to oocyte retrieval. In group B also, serum LH measurement was measured three times as group A. Transvaginal ultrasound guided oocyte pickup (OPU) was done 35 hr after the first dose agonist. Oocyte retrieval was done under general anesthesia with single lumen oocyte retrieval needle (Swemed, Vitrolife, Sweden). OHSS symptom assessment and transvaginal sonography was done on days 4 and 7 post pick-up to evaluate the ovarian size, free fluid in Douglas. IVF or intracytoplasmic sperm injection was done based on sperm parameter. Fertilization was assessed 18 hr. following IVF with the presence of 2 pronuclei (2PN).
The outcomes were oocyte yield, MI rate, MII rate, maturity rate, germinal vesicle (GV) rate, 2PN, and embryo yield OHSS rates and type were also assessed. Maturity rate was defined as the ratio of MII oocytes (presence of a polar body) to the total number of oocytes. Serum LH (IU/L), E2, and Progesterone (ng/mL) levels were compared between the two groups. All good-quality embryos were frozen.


4. Discussion
Oure results showed that the maturity rate, MI, MII, and GV oocytes were not statistically different between the two study groups. LH levels measured at 12 hr. post-trigger did not relate statistically significant with maturity rate in our participants also no empty follicular syndrome was reported. It is identified that the restart of meiosis at 18 hr. after the onset of LH surge (15), and for the highest oocyte maturation, LH concentration should be retained over a threshold for 14-27 hr. A shorter duration and low-level LH concentration post-trigger with single dose of GnRHa cannot maintain an LH level over threshold for 14-27 hr, thus insufficient to induce best oocyte maturation. This suboptimal response can be more probable in women with PCOS, a condition with hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis dysfunction. Deepika and colleagues claimed a repeat dose of GnRHa at this critical hour (12 hr) could preserve the amplitude and the duration of gonadotropin surge, thus optimizing the oocyte maturity (16). They obtained a significantly higher yield of MII oocytes along with a statistically significant lesser number of MIs and GV oocytes in the repeat dose group. Our study findings do not support these findings. In our study, maturity rate, MI, MII, and GV oocytes were not statistically different between the two study groups, which question the proposed mechanism in repeat dose protocol. Moreover, the LH levels measured at 12 hr post-trigger predicted oocyte maturity in Deepika and colleagues study (16). But this relationship was not approved in our analysis. So, we can say that LH level post-trigger cannot necessarily predict the oocyte maturity and so the second dose does not improve the outcome of oocyte maturity.
EFS is a complication of IVF. It’s thwarting for participants and leads to cycle cancelation. The etiopathophysiology of EFS is still unknown. It is reported as a complication in single-dose GnRHa trigger. Pituitary gland is the location of action for GnRHa and dysfunctions of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis might not make optimal flare leading to deficient final oocyte maturation and EFS (17). We proposed that a second dose of GnRH agonist after 12 hr. since the first dose could provide duration of surge and amplitude and as a result of that may improve oocyte maturity after the GnRHa trigger. In our participants, no EFS was reported to support our hypothesis.
Limitation
Our study had some limitations such as small sample size and missing reproductive outcomes. Overall, although one previous study with a proof-of-concept RCT suggested that a repeat dose of GnRHa 12 hr following the first dose in PCOS undergoing IVF delivers a better cycle outcome in terms of maturity of oocytes, higher number of blastocysts, and clinical pregnancy improvement, our RCT study revealed no difference between the repeat-dose and single-dose GnRHa trigger. Therefore, more RCT studies with large sample size and long follow-up is needed to evaluate the repeat dose effect more precisely.
Conclusion
Although, the second dose of GnRH agonist after 12 hr since the first dose could provide duration of LH surge and amplitude and as a result no empty follicular syndrome was seen, the maturity rate, MI, MII, and GV oocytes were not different between the two study groups.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Ms. Behnaz Gandom and Fahimeh Dehghanizadeh for assistance with data gathering.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Full-Text: (575 Views)
- Introduction
In addition, in PCOS women and hyper responders after GnRHa trigger, the gonadotropin answer is greatly shorter than endogenic LH surge in a natural cycle that causes more suboptimal expected answer (12, 13). The underlying mechanisms proposed are that some women with PCOS show neuro-endocrine abnormalities; moreover, the supraphysiologic estradiol (E2) level cause apparent increase in the number of follicles and insufficient number of LH receptor (14), therefore, a single dose of GnRHa might not lead to LH surge over a threshold level in these participants. In order to gain optimum responses, repeated dose 12 hr after starting doses of GnRHa resulted in terms of better maturity of oocytes, higher number of blastocysts, and higher clinical pregnancy in Deepikaand colleagues study. In a similar research, we aimed to evaluate if a second dose 12 hr. after the first dose of GnRH agonist trigger could provide long duration of LH surge and amplitude appropriately making an improvement in oocyte maturity.
The aim of this study was to see weather oocyte maturity will improve by a repeat dose of GnRHa or not?
- Materials and Methods
The inclusion criteria were 1) PCOS women outlined based on ESHRE ASRM Rotterdam criteria, 2) stimulation in a GnRH ant protocol, 3) age 20-38 yr, 4) E2 concentration > 3000 IU on trigger day, 5) Body Mass Index > 18 and < 30, 6) indication for IVF, and 7) participants’ desire
The exclusion criteria were 1) severe male factor, 2) uterine abnormally, 3) endometriosis, and 4) metabolic disease (ex. Diabetes).
- 1. Study protocol
Serum E2, LH, and progesterone concentration were measured on the trigger day when three lead follicles reached 17 mm in diameter. Participants with serum E2 > 3000 based on randomization table number were divided in two groups. Final oocyte maturation was triggered with a single dose of 0.2 mg sc triptorelin (decapeptyl) 34-36 hr. prior to oocyte retrieval in both groups. In group A, a repeat dose of 0.1 mg, 12 hr after the first dose was prescribed, but in group B, a single dose of GnRHa 0.2 mg sc triptorelin (decapeptyl) was given. In group A, serum LH was measured 12 hr. after the first dose of GnRHa administration, and then again after the second dose of GnRHa and prior to oocyte retrieval. In group B also, serum LH measurement was measured three times as group A. Transvaginal ultrasound guided oocyte pickup (OPU) was done 35 hr after the first dose agonist. Oocyte retrieval was done under general anesthesia with single lumen oocyte retrieval needle (Swemed, Vitrolife, Sweden). OHSS symptom assessment and transvaginal sonography was done on days 4 and 7 post pick-up to evaluate the ovarian size, free fluid in Douglas. IVF or intracytoplasmic sperm injection was done based on sperm parameter. Fertilization was assessed 18 hr. following IVF with the presence of 2 pronuclei (2PN).
The outcomes were oocyte yield, MI rate, MII rate, maturity rate, germinal vesicle (GV) rate, 2PN, and embryo yield OHSS rates and type were also assessed. Maturity rate was defined as the ratio of MII oocytes (presence of a polar body) to the total number of oocytes. Serum LH (IU/L), E2, and Progesterone (ng/mL) levels were compared between the two groups. All good-quality embryos were frozen.
- 2. Ethical consideration
- 3. Statistical analysis
- Results



4. Discussion
Oure results showed that the maturity rate, MI, MII, and GV oocytes were not statistically different between the two study groups. LH levels measured at 12 hr. post-trigger did not relate statistically significant with maturity rate in our participants also no empty follicular syndrome was reported. It is identified that the restart of meiosis at 18 hr. after the onset of LH surge (15), and for the highest oocyte maturation, LH concentration should be retained over a threshold for 14-27 hr. A shorter duration and low-level LH concentration post-trigger with single dose of GnRHa cannot maintain an LH level over threshold for 14-27 hr, thus insufficient to induce best oocyte maturation. This suboptimal response can be more probable in women with PCOS, a condition with hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis dysfunction. Deepika and colleagues claimed a repeat dose of GnRHa at this critical hour (12 hr) could preserve the amplitude and the duration of gonadotropin surge, thus optimizing the oocyte maturity (16). They obtained a significantly higher yield of MII oocytes along with a statistically significant lesser number of MIs and GV oocytes in the repeat dose group. Our study findings do not support these findings. In our study, maturity rate, MI, MII, and GV oocytes were not statistically different between the two study groups, which question the proposed mechanism in repeat dose protocol. Moreover, the LH levels measured at 12 hr post-trigger predicted oocyte maturity in Deepika and colleagues study (16). But this relationship was not approved in our analysis. So, we can say that LH level post-trigger cannot necessarily predict the oocyte maturity and so the second dose does not improve the outcome of oocyte maturity.
EFS is a complication of IVF. It’s thwarting for participants and leads to cycle cancelation. The etiopathophysiology of EFS is still unknown. It is reported as a complication in single-dose GnRHa trigger. Pituitary gland is the location of action for GnRHa and dysfunctions of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis might not make optimal flare leading to deficient final oocyte maturation and EFS (17). We proposed that a second dose of GnRH agonist after 12 hr. since the first dose could provide duration of surge and amplitude and as a result of that may improve oocyte maturity after the GnRHa trigger. In our participants, no EFS was reported to support our hypothesis.
Limitation
Our study had some limitations such as small sample size and missing reproductive outcomes. Overall, although one previous study with a proof-of-concept RCT suggested that a repeat dose of GnRHa 12 hr following the first dose in PCOS undergoing IVF delivers a better cycle outcome in terms of maturity of oocytes, higher number of blastocysts, and clinical pregnancy improvement, our RCT study revealed no difference between the repeat-dose and single-dose GnRHa trigger. Therefore, more RCT studies with large sample size and long follow-up is needed to evaluate the repeat dose effect more precisely.
Conclusion
Although, the second dose of GnRH agonist after 12 hr since the first dose could provide duration of LH surge and amplitude and as a result no empty follicular syndrome was seen, the maturity rate, MI, MII, and GV oocytes were not different between the two study groups.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Ms. Behnaz Gandom and Fahimeh Dehghanizadeh for assistance with data gathering.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Type of Study: Original Article |
Subject:
Assisted Reproductive Technologies
References
1. Itskovitz J, Boldes R, Levron J, Erlik Y, Kahana L, Brandes JM. Induction of preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge and prevention of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome by gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist. Fertil Steril 1991; 56: 213-220. [DOI:10.1016/S0015-0282(16)54474-4]
2. Gonen Y, Balakier H, Powell W, Casper RF. Use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist to trigger follicular maturation for in vitro fertilization. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1990; 71: 918-922. [DOI:10.1210/jcem-71-4-918] [PMID]
3. Eppig JJ. FSH stimulates hyaluronic acid synthesis by oocyte-cumulus cell complexes from mouse preovulatory follicles. Nature 1979; 281: 483-484. [DOI:10.1038/281483a0] [PMID]
4. Yding Andersen C. Effect of FSH and its different isoforms on maturation of oocytes from pre-ovulatory follicles. Reprod Biomed Online 2002; 5: 232-239. [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)61826-3]
5. Moyle WR, Bahl OP, Marz L. Role of carbohydrate of human chorionic gonadotropin in the mechanism of hormone action. J Biol Chem 1975; 250: 9163-9169.
6. Kol S. Luteolysis induced by a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist is the key to prevention of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. Fertil Steril 2004; 81: 1-5. [DOI:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2003.05.032] [PMID]
7. Humaidan P, Papanikolaou EG, Kyrou D, Alsbjerg B, Polyzos NP, Devroey P, et al. The luteal phase after GnRH-agonist triggering of ovulation: present and future perspectives. Reprod Biomed Online 2012; 24: 134-141. [DOI:10.1016/j.rbmo.2011.11.001] [PMID]
8. Yen SS, Llerena O, Little B, Pearson OH. Disappearance rates of endogenous luteinizing hormone and chorionic gonadotropin in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1968; 28: 1763-1767. [DOI:10.1210/jcem-28-12-1763] [PMID]
9. Humaidan P, Kol S, Papanikolaou EG; Copenhagen GnRH Agonist Triggering Workshop Group. GnRH agonist for triggering of final oocyte maturation: time for a change of practice? Hum Reprod Update 2011; 17: 510-524. [DOI:10.1093/humupd/dmr008] [PMID]
10. Griesinger G, Schultz L, Bauer T, Broessner A, Frambach T, Kissler S. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome prevention by gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist triggering of final oocyte maturation in a gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist protocol in combination with a "freeze-all" strategy: a prospective multicentric study. Fertil Steril 2011; 95: 2029-2033. [DOI:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2011.01.163] [PMID]
11. Castillo JC, Garcia-Velasco J, Humaidan P. Empty follicle syndrome after GnRHa triggering versus hCG triggering in COS. J Assist Reprod Genet 2012; 29: 249-253. [DOI:10.1007/s10815-011-9704-8] [PMID] [PMCID]
12. Itskovitz-Eldor J, Kol S, Mannaerts B. Use of a single bolus of GnRH agonist triptorelin to trigger ovulation after GnRH antagonist ganirelix treatment in women undergoing ovarian stimulation for assisted reproduction, with special reference to the prevention of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome: preliminary report: short communication. Hum Reprod 2000; 15: 1965-1968. [DOI:10.1093/humrep/15.9.1965] [PMID]
13. Engmann L, DiLuigi A, Schmidt D, Nulsen J, Maier D, Benadiva C. The use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist to induce oocyte maturation after cotreatment with GnRH antagonist in high-risk patients undergoing in vitro fertilization prevents the risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome: a prospective randomized controlled study. Fertil Steril 2008; 89: 84-91. [DOI:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2007.02.002] [PMID]
14. O'Neill KE, Senapati S, Dokras A. Use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist trigger during in vitro fertilization is associated with similar endocrine profiles and oocyte measures in women with and without polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril 2015; 103: 264-269. [DOI:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2014.09.042] [PMID] [PMCID]
15. Seibel MM, Smith DM, Levesque L, Borten M, Taymor ML. The temporal relationship between the luteinizing hormone surge and human oocyte maturation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1982; 142: 568-572. [DOI:10.1016/0002-9378(82)90763-3]
16. Deepika K, Baiju P, Gautham P, Suvarna R, Arveen V, Kamini R. Repeat dose of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist trigger in polycystic ovarian syndrome undergoing in vitro fertilization cycles provides a better cycle outcome - A proof-of-concept study. J Hum Reprod Sci 2017; 10: 271-280. [DOI:10.4103/jhrs.JHRS_102_17] [PMID] [PMCID]
17. Deepika K, Sindhuma D, Kiran B, Ravishankar N, Gautham P, Kamini R. Empty follicle syndrome following GnRHa trigger in PCOS patients undergoing IVF cycles. J Reprod Infertil 2018; 19: 16-25.
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |








