Sun, Feb 22, 2026
[Archive]
Volume 23, Issue 1 (January 2025)
IJRM 2025, 23(1): 55-66 |
Back to browse issues page
Ethics code: IR.UM.REC.1401.213
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Abbasi E, Behnam Rassouli M, Moghimi A, Neshati Z. The restorative effect of platelet-rich plasma on estrous cycle disruption induced by arcuate nucleus lesion in female Wistar rats: An experimental study. IJRM 2025; 23 (1) :55-66
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-3349-en.html
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-3349-en.html
1- Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran.
2- Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran. ,behnam@um.ac.ir
2- Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran. ,
Abstract: (883 Views)
Background: Successful reproduction relies on a functioning hypothalamic-pituitary-gonad axis. Damage to this axis disrupts the estrus cycle and reproductive capability.
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the effects of single or multiple platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections on repairing the damaged hypothalamic arcuate nucleus (ARC) and restoring the estrus cycle in Wistar rats.
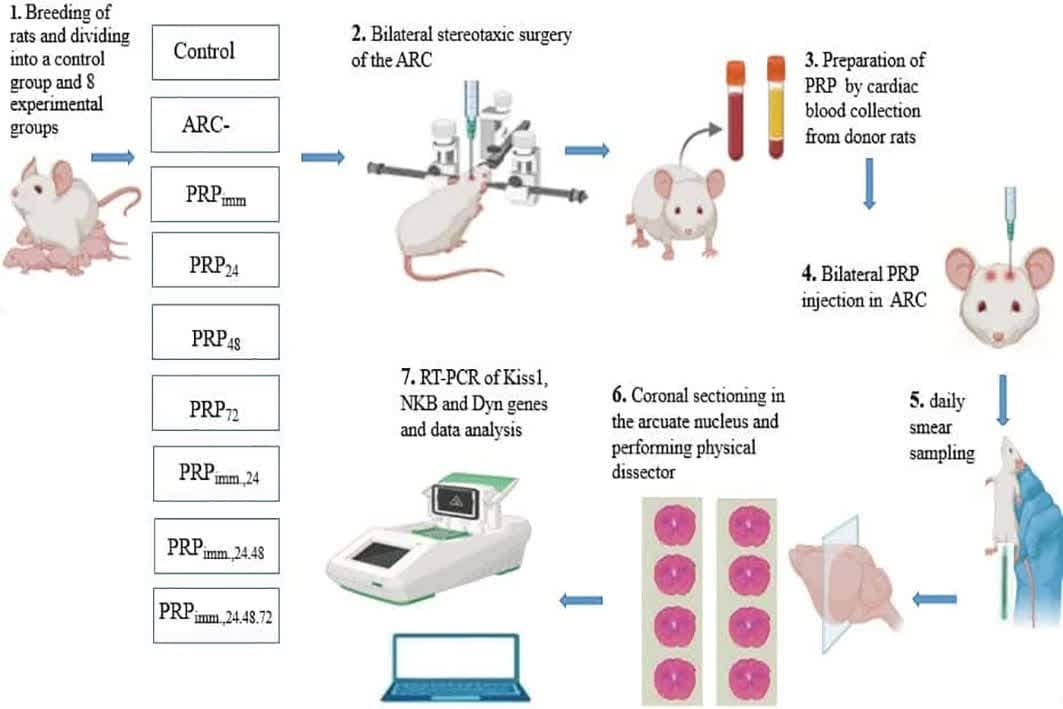
Materials and Methods: 90 female Wistar rats (2-3 months old, 250-280 gr) with regular estrous cycles were divided into a control group and 8 experimental groups (n = 10/each). After bilateral stereotaxic chemical surgery of the ARC using quinolinic acid (500 nmol/2 μl), the experimental rats were categorized into several treatment regimens: ARC- (no treatment), 1 PRP injection (immediately, 24 hr, 48 hr, and 72 hr postsurgery), 2 PRP injections (immediately, 24 hr), 3 PRP injections (immediately, 24 hr, and 48 hr), and 4 PRP injections (immediately, 24 hr, 48 hr, and 72 hr). Vaginal smear cytology was performed daily for 2.5 months. In the end, rats brains were removed and divided for real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis of kisspeptin, neurokinin B, and dynorphin, as well as for ARC cell counting.
Results: Vaginal smear cytology indicated that PRP administration gradually restored the estrous cycle. Compared to the ARC- group, PRP treatment significantly increased ARC cell density (p = 0.012) and mRNA levels of kisspeptin, neurokinin B, and dynorphin (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: These findings not only emphasized the importance of the ARC for the regularity of estrous cycle, but also showed the potential effects of local PRP treatment in contribution to the protection/reconstruction of ARC.
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the effects of single or multiple platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections on repairing the damaged hypothalamic arcuate nucleus (ARC) and restoring the estrus cycle in Wistar rats.
Materials and Methods: 90 female Wistar rats (2-3 months old, 250-280 gr) with regular estrous cycles were divided into a control group and 8 experimental groups (n = 10/each). After bilateral stereotaxic chemical surgery of the ARC using quinolinic acid (500 nmol/2 μl), the experimental rats were categorized into several treatment regimens: ARC- (no treatment), 1 PRP injection (immediately, 24 hr, 48 hr, and 72 hr postsurgery), 2 PRP injections (immediately, 24 hr), 3 PRP injections (immediately, 24 hr, and 48 hr), and 4 PRP injections (immediately, 24 hr, 48 hr, and 72 hr). Vaginal smear cytology was performed daily for 2.5 months. In the end, rats brains were removed and divided for real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis of kisspeptin, neurokinin B, and dynorphin, as well as for ARC cell counting.
Results: Vaginal smear cytology indicated that PRP administration gradually restored the estrous cycle. Compared to the ARC- group, PRP treatment significantly increased ARC cell density (p = 0.012) and mRNA levels of kisspeptin, neurokinin B, and dynorphin (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: These findings not only emphasized the importance of the ARC for the regularity of estrous cycle, but also showed the potential effects of local PRP treatment in contribution to the protection/reconstruction of ARC.
This article has been extracted from Ph.D. Thesis. (Elham Abbasi)
Type of Study: Original Article |
Subject:
Reproductive Physiology
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |