Thu, Jan 29, 2026
[Archive]
Volume 23, Issue 11 (November 2025)
IJRM 2025, 23(11): 927-936 |
Back to browse issues page
Ethics code: IR.MUI.PHANUT.REC.1402.098
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Shirani M, Bagherniya M, Sadeghi O, Ghasemi Tehrani H, Eskandari M H, Sharma M et al . Effects of supplementation with two probiotic strains on metabolic profile, hormonal status, oxidative stress, and quality of life in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A study protocol for a randomized clinical trial. IJRM 2025; 23 (11) :927-936
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-3685-en.html
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-3685-en.html
Mahsa Shirani1 

 , Mohammad Bagherniya1
, Mohammad Bagherniya1 

 , Omid Sadeghi2
, Omid Sadeghi2 

 , Hatav Ghasemi Tehrani3
, Hatav Ghasemi Tehrani3 

 , Mohammad Hadi Eskandari4
, Mohammad Hadi Eskandari4 

 , Manoj Sharma5
, Manoj Sharma5 

 , Gholamreza Askari *6
, Gholamreza Askari *6 




 , Mohammad Bagherniya1
, Mohammad Bagherniya1 

 , Omid Sadeghi2
, Omid Sadeghi2 

 , Hatav Ghasemi Tehrani3
, Hatav Ghasemi Tehrani3 

 , Mohammad Hadi Eskandari4
, Mohammad Hadi Eskandari4 

 , Manoj Sharma5
, Manoj Sharma5 

 , Gholamreza Askari *6
, Gholamreza Askari *6 


1- Nutrition and Food Security Research Center, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran. & Department of Community Nutrition, School of Nutrition and Food Science, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran.
2- Research Center for Food Hygiene and Safety, School of Public Health, Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences, Yazd, Iran. & Nutrition and Food Security Research Center, Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences, Yazd, Iran.
3- Isfahan Medical Obstetrics and Gynecology Group, Reproductive Sciences and Sexual Health Research Center, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran.
4- Department of Food Science and Technology, School of Agriculture, Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran.
5- Department of Social and Behavioral Health, School of Public Health, University of Nevada, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA. & Department of Internal Medicine, Kirk Kerkorian School of Medicine, University of Nevada, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA.
6- Nutrition and Food Security Research Center, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran. & Department of Community Nutrition, School of Nutrition and Food Science, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran. ,askari@mui.ac.ir
2- Research Center for Food Hygiene and Safety, School of Public Health, Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences, Yazd, Iran. & Nutrition and Food Security Research Center, Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences, Yazd, Iran.
3- Isfahan Medical Obstetrics and Gynecology Group, Reproductive Sciences and Sexual Health Research Center, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran.
4- Department of Food Science and Technology, School of Agriculture, Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran.
5- Department of Social and Behavioral Health, School of Public Health, University of Nevada, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA. & Department of Internal Medicine, Kirk Kerkorian School of Medicine, University of Nevada, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA.
6- Nutrition and Food Security Research Center, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran. & Department of Community Nutrition, School of Nutrition and Food Science, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran. ,
Abstract: (50 Views)
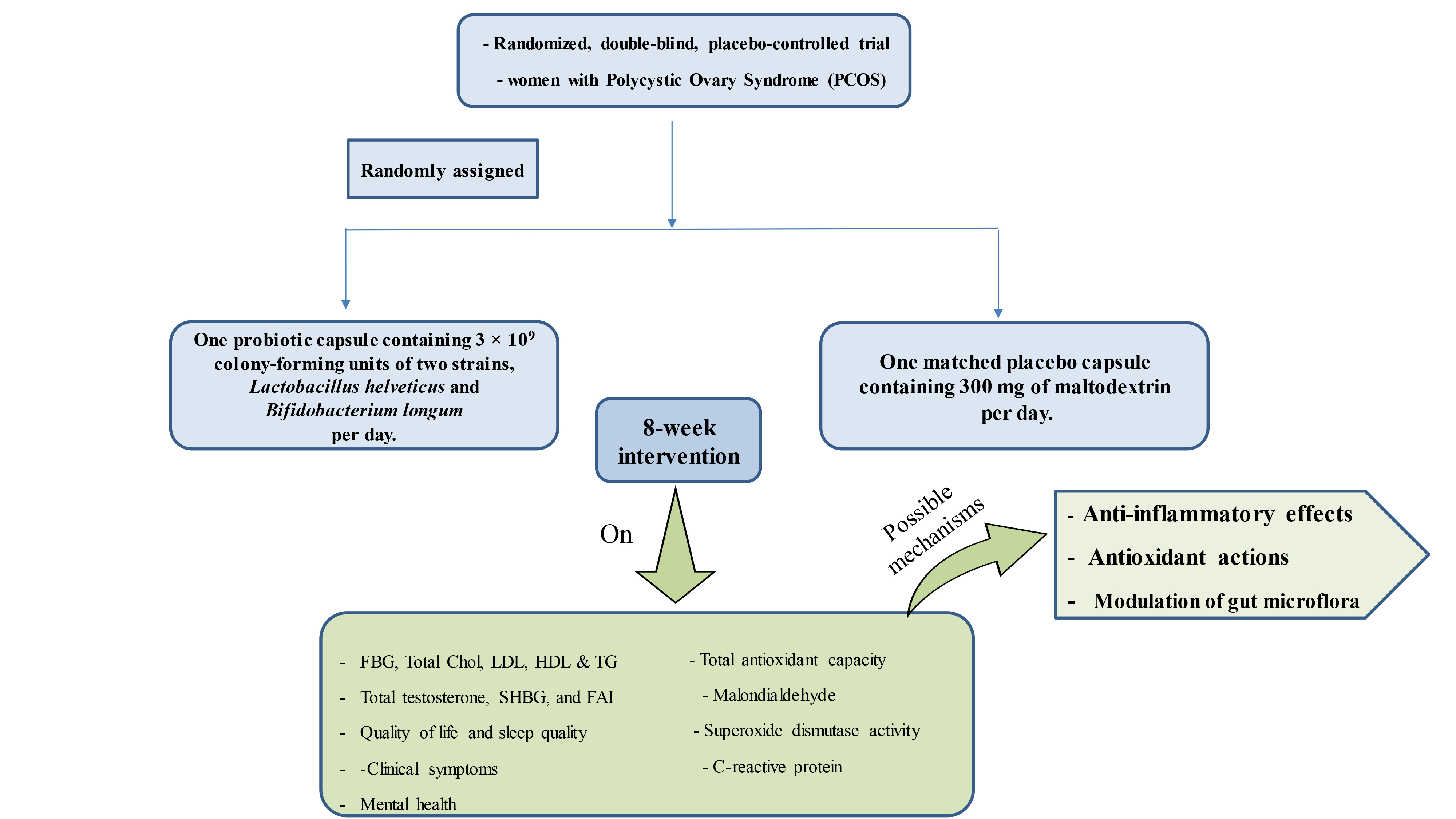
Background: Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine disorder in women, associated with insulin resistance, ovulatory dysfunction, hyperandrogenism, and inflammation. Current treatments often focus on symptoms rather than underlying causes, emphasizing the need for comprehensive strategies. Recently, probiotics have emerged as a safe and cost-effective nutritional option for managing metabolic issues.
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the effects of Lactobacillus helveticus and Bifidobacterium longum supplementation on the cardiometabolic profile, hormonal status, oxidative stress, and quality of life in women with PCOS.
Materials and Methods: We will conduct a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial involving 90 women with PCOS from Shahid Beheshti hospital, Isfahan, Iran. Recruitment will begin on June 20, 2024, and is expected to be completed by June 20, 2025. Participants will be randomly assigned to receive either a daily probiotic capsule containing Lactobacillus helveticus and Bifidobacterium longum or a placebo. The study will assess the impact of these probiotic strains on cardiometabolic profile, hormonal status, oxidative stress, mental health, quality of life, sleep quality, and clinical symptoms in women with PCOS. All parameters will be evaluated before and after the intervention.
Discussion: Elevated insulin levels and gut microbiota imbalances significantly contribute to the development of PCOS. Growing evidence suggests that gut dysbiosis is linked to sex hormone levels and estrous cycles. We hypothesize that probiotic supplementation in individuals with PCOS will improve hormonal, metabolic, inflammatory, and antioxidant markers compared to those receiving a placebo.
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the effects of Lactobacillus helveticus and Bifidobacterium longum supplementation on the cardiometabolic profile, hormonal status, oxidative stress, and quality of life in women with PCOS.
Materials and Methods: We will conduct a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial involving 90 women with PCOS from Shahid Beheshti hospital, Isfahan, Iran. Recruitment will begin on June 20, 2024, and is expected to be completed by June 20, 2025. Participants will be randomly assigned to receive either a daily probiotic capsule containing Lactobacillus helveticus and Bifidobacterium longum or a placebo. The study will assess the impact of these probiotic strains on cardiometabolic profile, hormonal status, oxidative stress, mental health, quality of life, sleep quality, and clinical symptoms in women with PCOS. All parameters will be evaluated before and after the intervention.
Discussion: Elevated insulin levels and gut microbiota imbalances significantly contribute to the development of PCOS. Growing evidence suggests that gut dysbiosis is linked to sex hormone levels and estrous cycles. We hypothesize that probiotic supplementation in individuals with PCOS will improve hormonal, metabolic, inflammatory, and antioxidant markers compared to those receiving a placebo.
Keywords: Probiotics, Polycystic ovary syndrome, Testosterone, Sex hormone-binding globulin, Randomized clinical trial.
Type of Study: Original Article |
Subject:
Fertility & Infertility
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |