Thu, Jan 8, 2026
[Archive]
Volume 6, Issue 2 (7-2008)
IJRM 2008, 6(2): 19-0 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Arefi S, Soltanghoraee H, Zarnani A H, Sadeghpour Tabaei A, Ghaffari Novin M, Zeraati H et al . Repeated IVF/ICSI-ETs failures and impact of hysteroscopy. IJRM 2008; 6 (2) :19-0
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-96-en.html
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-96-en.html
Soheila Arefi1 
 , Haleh Soltanghoraee *2
, Haleh Soltanghoraee *2 
 , Amir Hassan Zarnani1
, Amir Hassan Zarnani1 
 , Ali Sadeghpour Tabaei3
, Ali Sadeghpour Tabaei3 
 , Marefat Ghaffari Novin4
, Marefat Ghaffari Novin4 
 , Hojat Zeraati5
, Hojat Zeraati5 
 , Pegah Ebadi6
, Pegah Ebadi6 


 , Haleh Soltanghoraee *2
, Haleh Soltanghoraee *2 
 , Amir Hassan Zarnani1
, Amir Hassan Zarnani1 
 , Ali Sadeghpour Tabaei3
, Ali Sadeghpour Tabaei3 
 , Marefat Ghaffari Novin4
, Marefat Ghaffari Novin4 
 , Hojat Zeraati5
, Hojat Zeraati5 
 , Pegah Ebadi6
, Pegah Ebadi6 

1- Reproductive Immunology Department, Reproductive Biotechnology Research Center, Avicenna Research Institute, Avesina Infertility Center, Tehran, Iran
2- Genetic Departement, Reproductive Biotechnology Research Center, Avicenna Research Institute, Avesina Infertility Center, Tehran, Iran
3- Iran University, Shahid Rajaei Hospital, Tehran, Iran
4- Cellular and Molecular Biology Research Center, Shaheed Beheshti University (M.C.), Tehran, Iran
5- Tehran University of Medical Sciences, School of Public Health, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics
6- Reproductive Endocrinology and Embryology Departement, Reproductive Biotechnology Research Center, Avicenna Research Institute, Avesina Infertility Center, Tehran, Iran
2- Genetic Departement, Reproductive Biotechnology Research Center, Avicenna Research Institute, Avesina Infertility Center, Tehran, Iran
3- Iran University, Shahid Rajaei Hospital, Tehran, Iran
4- Cellular and Molecular Biology Research Center, Shaheed Beheshti University (M.C.), Tehran, Iran
5- Tehran University of Medical Sciences, School of Public Health, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics
6- Reproductive Endocrinology and Embryology Departement, Reproductive Biotechnology Research Center, Avicenna Research Institute, Avesina Infertility Center, Tehran, Iran
Keywords: Hysteroscopy, Repeated IVF/ICSI -ET failure
Full-Text [PDF 128 kb]
(719 Downloads)
| Abstract (HTML) (3819 Views)
Full-Text: (489 Views)
Introduction
Although there was gradual increase in the success of reproduction, over the years, but many couples also had been left frustrated following repeated failed attempts. Clinicians who treated unsuccessful couples often face a challenge.
The probable causes of repeated IVF failures were classified as: reduced endometrial receptivity, embryonic defects or multifactorial causes (1). Intrauterine and endometrial integrity abnormalities such as thin endometrium, altered expression of adhesive molecules and immunological factors like Anti Sperm (ASA), Anticardiolipin (aCL), Lupus anticoagulant (LA), Anti-Phosphatidylserine (aPS) , Anti-Phosphatidyl-ethanolamine (aPE), and Antinuclear antibody (ANA), Anti DNA, Anti Zona and Anti ovarian (AOA) antibodies (2), Thrombophilia (3), decrease expression of endometrial integrins, increase of natural killer cells activities and imbalance of cytokine networks (balance between IL-12 and IL-18) (4), may decrease endometrial receptivity, whereas chromosomal and genetic abnormalities of the male sperm or female ovarian defects, embryonic aneuploidia or zona hardening are embryonic reasons for the failure of implantation (5,6). Among the various etiologies that were described, endometrial regularity played an important role in infertility and success of IVF programs.
Hysterosalpingography (HSG) is sensitive but its specificity for detection of intrauterine abnormalities is low (23%), with a false positive rate of 44% and false negative rate of 10% (7). Transvaginal sonography (TVS) is more specific (96.3%) and sensitive (81.8%) than HSG with negative (97.6%) and positive (73.8%) predictive values for the detection of any intrauterine abnormalities (8, 9). Accordingly, saline infusion sonohysterography (SIS), is an accurate and safe method in the evaluation of the uterine cavity (10). Kelekci et al showed equal accuracy between hysteroscopy and SIS but lower pain score in saline infusion sonography (11). Although SIS showed high failure rate in Rogerson study (12), however hysteroscopy showed to be more accurate in the evaluation of intracavity pathology in comparison with other clinical studies (8). Treatment of these abnormalities prior to the subsequent IVF/ICSI-ET raises the pregnancy rate to 22% in Golan and Schiano et al studies (7, 13).
Although the previous trials showed the usefulness of uterine reassessment by hysteroscopy in women with two IVF failures, (14-16) but they didn’t exclude the other probable contributory factors like thrombophilia and immunological disorders.
In the present observational study we evaluated hysteroscopy abnormalities; and also the subsequent IVF/ICSI-ET outcome in patients with unexplained repeated IVF/ICSI-ET failure after excluding all other possible ethological factors.
Materials and methods
Ethics of experimentation
Investigations have been approved and the trial has been authorized under the decision of Ethical Committee of Avicenna Research Institute.
Patients
This study was performed from July 2003 to October 2006, at the Avicenna Infertility Clinic on infertile women (25-38 years old) who referred to the clinic with the history of more than two previous IVF/ICSI-ET failures despite transfer of a minimum three good-quality embryos in each attempt. After taking history and physical exam; HSG , and routine hematological, biochemical and hormonal tests, semen analysis, and also flowcytometry , autoantibodies profile like Anti-Cardiolipin (aCL), Lupus Anticoagulant (LA), Anti-Phosphatidylserine (aPS), Anti-Phosphatidyl-ethanolamine (aPE), and Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA), Anti DNA , and thrombopholia profile like MTHFR gene, prothrombine gene, Factor V leiden gene, serum homocystein, protein C, Protein S, anti-thrombin 3 and karyotype have accomplished in all women referred to our clinic with more than two IVF/ICSI-ET failures. All infertile women underwent standard TVS (Pie medical, model 260 Corvus) with convex 7.5 MHz transvaginal ultrasound probe. We excluded untreated HSG shown abnormalities, thrombophilia, immunological and, genetic problems, and also severe male factor infertility in selected patients of our study.
Measurements
We informed all cases about the technique, therapeutic effect and potential risks (informed consent) of hysteroscopy and obtained informed consent. The selected patients underwent a diagnostic and/or operative hysteroscopy in early follicular phase of the cycle and all procedures were done between the 7th and 11th day of the cycle. The interventions were performed under general anesthesia in normal lithotomic position. After cervical dilatation of 5-9 mm, operative rigid hysteroscope (Olympus) was entered under visual control into the uterine cavity. A continuous flow instrument with separate in- and out-flow channel was used which was connected to a video camera system. Dextrose 5% was used for distention medium, keeping the distention pressure between 100-150 mmHg. Duration of the procedure was kept as short as possible with continuous surveillance of the fluid balance. Intrauterine adhesions, polyps, and submucosal myomas were treated by scissor and resectoscope during hysteroscopic evaluation procedure; and by curettage after hysteroscopy in the cases with endometrial hyperplasia. Endometrial biopsy has been done in the cases of uterine cavity hypoplasia during hysteroscopy. The given findings in hysteroscopy have been analyzed.
Protocol of stimulation in subsequent IVF/ICSI attempt
Two months after hysteroscopy, the patients underwent ovarian stimulation with standard long protocol. GnRH–agonist (Buserlin: superfact, Aventis Pharma, Germany 0.5 mg/day) was administered from the day 21 of the cycle. Then all the patients were treated with human menopausal gonadotropin (hMG: Merional, IBSA, Switzerland, 150-300 IU/day) from day 2-3 of the next cycle, while continuing superfact 0.25 mg/day, with the control of follicular growth under sonography every 3-4 days. HCG was administered 10000 IU when the minimum of 3 leading follicles reached 16-18 mm, and 36 hours later oocyte collection was performed.
Statistical analysis
Data were expressed as mean values ± SD for numerical variables and in percentage for categorized variables. The data were analyzed with SPSS software and Fisher exact, chi-square, and MC-Nemar tests.
Results
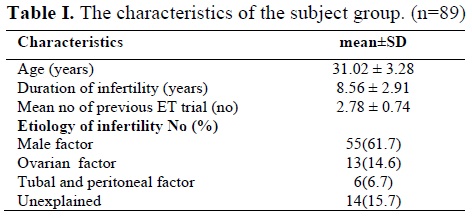
The etiologies of infertility in the study group have been shown in table I. The study population consisted of 89 infertile women, with the mean age of (31.02 ± 3.28) years, mean duration of infertility (8.56 ± 2.91) years and mean numbers of previous ET attempts were (2.78 ± 0.74).
However hysteroscopy showed to be more sensitive and specific in the evaluation of intracavity pathology in comparison with TVS in patients with the history of repeated IVF/ICSI-ET failures after exclusion of other possible caus.
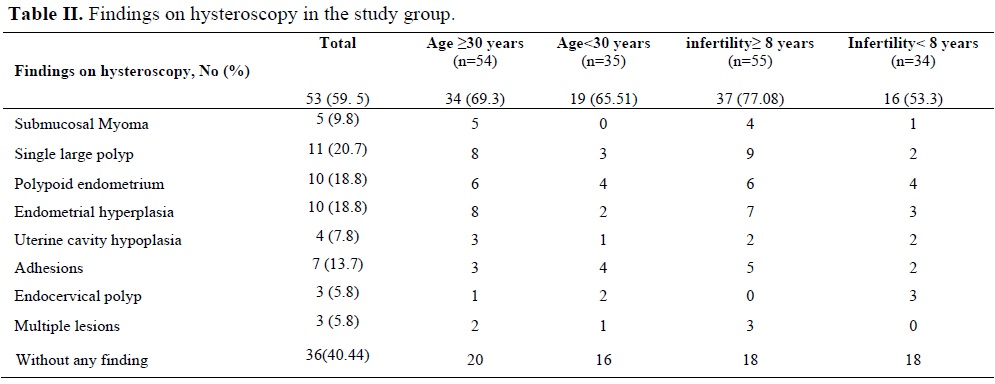
Single polyp and endometrial hyperplasia have been found more in patients more than 30 years old and with more than 8 years infertility, but it was not significant by using Fisher exact test (one tail) (p=0.27). Abnormal findings in patients with ≥30 years were not significant compared with younger patients, using chi-square=0.44 (p=0.51). More hysteroscopy abnormalities were found in the infertile patients with more than 8 years infertility, (chi-square=4.7, p=0.03), which was significant.
Structural abnormalities correlated with the presence of pathological abnormalities were seen in 94.3% (n=50) of cases. Also in 13.2% (n=7) of cases, nonspecific endometritis was reported. We had no early or late, major or even minor complications in our series.
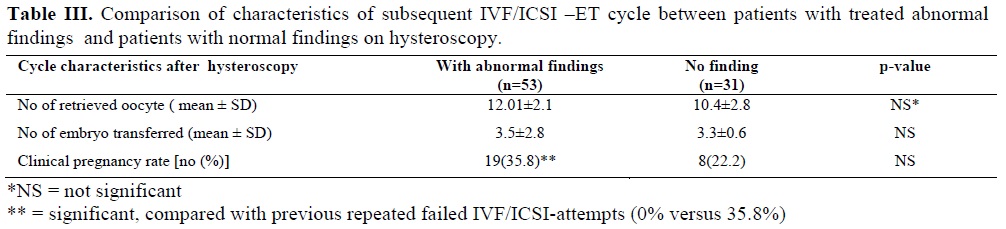
In patients with abnormal findings in hysteroscopy, subsequent IVF/ICSI-ET cycles after the procedure resulted significantly higher pregnancy rate, compared with previous failed attempts (35.8% versus 0%, p<0.001), although, there were not statistically significant difference in pregnancy rate between the patients with abnormal findings compared with whom with normal findings in hysteroscopy (35.8% versus 22.2, p=0.17, k2=1.88).
Discussion
TVS is the first clinical diagnostic test in the investigation of the uterine cavity and is especially important as a noninvasive technique to plan hysteroscopy. The sensitivity, specificity, and positive (PPV) and negative predictive values (NPV) for TVS in detecting abnormal uterine cavities have been shown as 100%, 96.3%, 91.3%, and 100%, respectively (8). However SIS is superior to pelvic ultrasound in detecting intracavitary pathology (17). TVS had sensitivity of 72%, specificity of 92%, PPV of 94% and NPV of 65%, while SIS had sensitivity of 94.1%, specificity of 95%, PPV of 96% and NPV of 90% (18). Hysteroscopy is a gold standard instrument, offers diagnostic accuracy for evaluating the uterine characteristics with the ability to treat uterine pathology in infertile women especially in patients with repeated IVF failures (19), although; it couldn’t show the functional status of the endometrium. Ragni et al compared the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of TVS and hysteroscopy (20).
The TVS`s sensitivity and specificity in comparison with hysteroscopy were 91% and 83% respectively. The false positive rate was 9.2% and a 5.1% false negative rate was detected compared to hysteroscopy. Also Hauge et al showed that hysteroscopy and TVS findings were similar in 90.9% (9). Our study showed TVS is specific, but not sensitive compared to the hysteroscopy. Capability to obtain a direct view of the uterine cavity by hysteroscopy showed to be more accurate in the evaluation of intracavity pathology in patients with unexplained IVF failures. Previous studies reported a high incidence of intrauterine abnormalities in patients undergoing IVF/ICSI-ET.
Faghali et al evaluated the benefits of a diagnostic hysteroscopy prior to IVF which shows the systematic hysteroscopy prior to IVF could improve the pregnancy rate (21). La Sala and Oliveira et al showed relation between IVF-ET failure and unsuspected intrauterine abnormalities (22, 23).
Makris et al performed hysteroscopy in patients with history of abortions, infertility and repeated failure of IVF. They showed that abnormal hysteroscopic findings were observed in 40.5% of cases in which intrauterine adhesions, endometrial hyperplasia and polyps were the most common (16). According to the results of our study, abnormal hysteroscopic findings were observed in 59.5% of the cases with unexplained repeated IVF failures which is higher than the result of previous studies due to exclusion of the other possible reasons of repeated ET failures like, thromobophilia, chromosomal and immunologic factors. Dicker et al showed, uterine abnormalities were detected in about 18% women with normal initial hysteroscopy who had three or more IVF-ET failures and underwent repeated hysteroscopy (15).
Also Schiano et al showed abnormalities in half of the cases like cervical abnormalities (synechia, polyp, and false passage) and hormonal-dependent abnormalities (polyp, hyperplasia, submucous myoma) in repeated uterine hysteroscopy after two implantation failures in IVF (13). Operative hysteroscopy showed to be effective in the treatment of intra-uterine adhesions with infertility in Kdous study with good results in achieving pregnancy (24).
Pabuccu et al observed quite an improvement in access to the endometrial cavity during ET procedure after the hysteroscopic shaving procedure in patients with difficult ETs and failed IVFs attempts due to cervical stenosis (25). We treated the structural abnormalities at the time of hysteroscopy and we had no early or late, major or even minor complications in our series. The pathological reports confirmed the observed lesions in 94.7% comparable to the results of Woolcott study (26).
Dicker study showed, that in elderly women, age-related uterine pathology such as submucous myoma, endometrial hyperplasia, and polyps were more prominent, while in younger patients other uterine lesions such as adhesions and tubal ostia occlusion were more common (15). In our experiences, we have seen single polyp and endometrial hyperplasia more in the patients with ≥30years olds rather than the younger group (p- value= 0.78). Also there were more abnormalities especially single polyp, polypoid endometrium and also endometrial hyperplasia in group of the patient with more than 8 years infertility (p-values: 0.08, 0.6, and 0.12, respectively).
According to the result of our study, treatment of the endometrial pathology resulted 34.8% pregnancy rate in the subsequent IVF/ICSI-ET, which is more than the results of Golan (22%) (7), Mihaila (16.6) (19) and Schiano (22%) (13) .This difference seems to be attributed to the exclusion all other factor related to IVF failure, which limited performing hysteroscopy with best result just in patients with endometrial pathology.
Conclusion
TVS showed as a noninvasive, specific but not sensitive method for detecting intracavitary pathology. Hysteroscopy proved to be a very useful, accurate and safe method of assessing and treatment of uterine and endometrial pathologies in patients with repeated IVF/ICSI-ET failures after excluding other possible reason for implantation failure, although it couldn’t evaluate uterine and endometrial functional status.
Acknowledgment
The author wishes to thank the staff of Avesina Infertility Center especially Dr. Akhondi and Dr. Modaberi for their cooperation.
Although there was gradual increase in the success of reproduction, over the years, but many couples also had been left frustrated following repeated failed attempts. Clinicians who treated unsuccessful couples often face a challenge.
The probable causes of repeated IVF failures were classified as: reduced endometrial receptivity, embryonic defects or multifactorial causes (1). Intrauterine and endometrial integrity abnormalities such as thin endometrium, altered expression of adhesive molecules and immunological factors like Anti Sperm (ASA), Anticardiolipin (aCL), Lupus anticoagulant (LA), Anti-Phosphatidylserine (aPS) , Anti-Phosphatidyl-ethanolamine (aPE), and Antinuclear antibody (ANA), Anti DNA, Anti Zona and Anti ovarian (AOA) antibodies (2), Thrombophilia (3), decrease expression of endometrial integrins, increase of natural killer cells activities and imbalance of cytokine networks (balance between IL-12 and IL-18) (4), may decrease endometrial receptivity, whereas chromosomal and genetic abnormalities of the male sperm or female ovarian defects, embryonic aneuploidia or zona hardening are embryonic reasons for the failure of implantation (5,6). Among the various etiologies that were described, endometrial regularity played an important role in infertility and success of IVF programs.
Hysterosalpingography (HSG) is sensitive but its specificity for detection of intrauterine abnormalities is low (23%), with a false positive rate of 44% and false negative rate of 10% (7). Transvaginal sonography (TVS) is more specific (96.3%) and sensitive (81.8%) than HSG with negative (97.6%) and positive (73.8%) predictive values for the detection of any intrauterine abnormalities (8, 9). Accordingly, saline infusion sonohysterography (SIS), is an accurate and safe method in the evaluation of the uterine cavity (10). Kelekci et al showed equal accuracy between hysteroscopy and SIS but lower pain score in saline infusion sonography (11). Although SIS showed high failure rate in Rogerson study (12), however hysteroscopy showed to be more accurate in the evaluation of intracavity pathology in comparison with other clinical studies (8). Treatment of these abnormalities prior to the subsequent IVF/ICSI-ET raises the pregnancy rate to 22% in Golan and Schiano et al studies (7, 13).
Although the previous trials showed the usefulness of uterine reassessment by hysteroscopy in women with two IVF failures, (14-16) but they didn’t exclude the other probable contributory factors like thrombophilia and immunological disorders.
In the present observational study we evaluated hysteroscopy abnormalities; and also the subsequent IVF/ICSI-ET outcome in patients with unexplained repeated IVF/ICSI-ET failure after excluding all other possible ethological factors.
Materials and methods
Ethics of experimentation
Investigations have been approved and the trial has been authorized under the decision of Ethical Committee of Avicenna Research Institute.
Patients
This study was performed from July 2003 to October 2006, at the Avicenna Infertility Clinic on infertile women (25-38 years old) who referred to the clinic with the history of more than two previous IVF/ICSI-ET failures despite transfer of a minimum three good-quality embryos in each attempt. After taking history and physical exam; HSG , and routine hematological, biochemical and hormonal tests, semen analysis, and also flowcytometry , autoantibodies profile like Anti-Cardiolipin (aCL), Lupus Anticoagulant (LA), Anti-Phosphatidylserine (aPS), Anti-Phosphatidyl-ethanolamine (aPE), and Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA), Anti DNA , and thrombopholia profile like MTHFR gene, prothrombine gene, Factor V leiden gene, serum homocystein, protein C, Protein S, anti-thrombin 3 and karyotype have accomplished in all women referred to our clinic with more than two IVF/ICSI-ET failures. All infertile women underwent standard TVS (Pie medical, model 260 Corvus) with convex 7.5 MHz transvaginal ultrasound probe. We excluded untreated HSG shown abnormalities, thrombophilia, immunological and, genetic problems, and also severe male factor infertility in selected patients of our study.
Measurements
We informed all cases about the technique, therapeutic effect and potential risks (informed consent) of hysteroscopy and obtained informed consent. The selected patients underwent a diagnostic and/or operative hysteroscopy in early follicular phase of the cycle and all procedures were done between the 7th and 11th day of the cycle. The interventions were performed under general anesthesia in normal lithotomic position. After cervical dilatation of 5-9 mm, operative rigid hysteroscope (Olympus) was entered under visual control into the uterine cavity. A continuous flow instrument with separate in- and out-flow channel was used which was connected to a video camera system. Dextrose 5% was used for distention medium, keeping the distention pressure between 100-150 mmHg. Duration of the procedure was kept as short as possible with continuous surveillance of the fluid balance. Intrauterine adhesions, polyps, and submucosal myomas were treated by scissor and resectoscope during hysteroscopic evaluation procedure; and by curettage after hysteroscopy in the cases with endometrial hyperplasia. Endometrial biopsy has been done in the cases of uterine cavity hypoplasia during hysteroscopy. The given findings in hysteroscopy have been analyzed.
Protocol of stimulation in subsequent IVF/ICSI attempt
Two months after hysteroscopy, the patients underwent ovarian stimulation with standard long protocol. GnRH–agonist (Buserlin: superfact, Aventis Pharma, Germany 0.5 mg/day) was administered from the day 21 of the cycle. Then all the patients were treated with human menopausal gonadotropin (hMG: Merional, IBSA, Switzerland, 150-300 IU/day) from day 2-3 of the next cycle, while continuing superfact 0.25 mg/day, with the control of follicular growth under sonography every 3-4 days. HCG was administered 10000 IU when the minimum of 3 leading follicles reached 16-18 mm, and 36 hours later oocyte collection was performed.
Statistical analysis
Data were expressed as mean values ± SD for numerical variables and in percentage for categorized variables. The data were analyzed with SPSS software and Fisher exact, chi-square, and MC-Nemar tests.
Results
The etiologies of infertility in the study group have been shown in table I. The study population consisted of 89 infertile women, with the mean age of (31.02 ± 3.28) years, mean duration of infertility (8.56 ± 2.91) years and mean numbers of previous ET attempts were (2.78 ± 0.74).

Abnormal TVS findings were observed in 47 cases (52.8%) in which endometrial irregularity 17(36.1%), hyperplasia 14(29.7%), polyps 11(23.4%) and myoma 6(6.4%) were detected. Abnormal hysteroscopy findings were observed in 53 cases (59.5%) in which intrauterine adhesions, endometrial hyperplasia, polyps, were the most common abnormalities rather than submucosal myoma, uterine cavity hypoplasia, and endocervical polyps (Table II). According to our results, using Mc-Nemar test (χ2=4, p<0.5), sonography is more specific (100%) but not sensitive (88.6%) compared to the hysteroscopy, with false negative rate of 19.4%.


However hysteroscopy showed to be more sensitive and specific in the evaluation of intracavity pathology in comparison with TVS in patients with the history of repeated IVF/ICSI-ET failures after exclusion of other possible caus.
Single polyp and endometrial hyperplasia have been found more in patients more than 30 years old and with more than 8 years infertility, but it was not significant by using Fisher exact test (one tail) (p=0.27). Abnormal findings in patients with ≥30 years were not significant compared with younger patients, using chi-square=0.44 (p=0.51). More hysteroscopy abnormalities were found in the infertile patients with more than 8 years infertility, (chi-square=4.7, p=0.03), which was significant.
Structural abnormalities correlated with the presence of pathological abnormalities were seen in 94.3% (n=50) of cases. Also in 13.2% (n=7) of cases, nonspecific endometritis was reported. We had no early or late, major or even minor complications in our series.
In patients with abnormal findings in hysteroscopy, subsequent IVF/ICSI-ET cycles after the procedure resulted significantly higher pregnancy rate, compared with previous failed attempts (35.8% versus 0%, p<0.001), although, there were not statistically significant difference in pregnancy rate between the patients with abnormal findings compared with whom with normal findings in hysteroscopy (35.8% versus 22.2, p=0.17, k2=1.88).
Discussion
TVS is the first clinical diagnostic test in the investigation of the uterine cavity and is especially important as a noninvasive technique to plan hysteroscopy. The sensitivity, specificity, and positive (PPV) and negative predictive values (NPV) for TVS in detecting abnormal uterine cavities have been shown as 100%, 96.3%, 91.3%, and 100%, respectively (8). However SIS is superior to pelvic ultrasound in detecting intracavitary pathology (17). TVS had sensitivity of 72%, specificity of 92%, PPV of 94% and NPV of 65%, while SIS had sensitivity of 94.1%, specificity of 95%, PPV of 96% and NPV of 90% (18). Hysteroscopy is a gold standard instrument, offers diagnostic accuracy for evaluating the uterine characteristics with the ability to treat uterine pathology in infertile women especially in patients with repeated IVF failures (19), although; it couldn’t show the functional status of the endometrium. Ragni et al compared the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of TVS and hysteroscopy (20).
The TVS`s sensitivity and specificity in comparison with hysteroscopy were 91% and 83% respectively. The false positive rate was 9.2% and a 5.1% false negative rate was detected compared to hysteroscopy. Also Hauge et al showed that hysteroscopy and TVS findings were similar in 90.9% (9). Our study showed TVS is specific, but not sensitive compared to the hysteroscopy. Capability to obtain a direct view of the uterine cavity by hysteroscopy showed to be more accurate in the evaluation of intracavity pathology in patients with unexplained IVF failures. Previous studies reported a high incidence of intrauterine abnormalities in patients undergoing IVF/ICSI-ET.
Faghali et al evaluated the benefits of a diagnostic hysteroscopy prior to IVF which shows the systematic hysteroscopy prior to IVF could improve the pregnancy rate (21). La Sala and Oliveira et al showed relation between IVF-ET failure and unsuspected intrauterine abnormalities (22, 23).
Makris et al performed hysteroscopy in patients with history of abortions, infertility and repeated failure of IVF. They showed that abnormal hysteroscopic findings were observed in 40.5% of cases in which intrauterine adhesions, endometrial hyperplasia and polyps were the most common (16). According to the results of our study, abnormal hysteroscopic findings were observed in 59.5% of the cases with unexplained repeated IVF failures which is higher than the result of previous studies due to exclusion of the other possible reasons of repeated ET failures like, thromobophilia, chromosomal and immunologic factors. Dicker et al showed, uterine abnormalities were detected in about 18% women with normal initial hysteroscopy who had three or more IVF-ET failures and underwent repeated hysteroscopy (15).
Also Schiano et al showed abnormalities in half of the cases like cervical abnormalities (synechia, polyp, and false passage) and hormonal-dependent abnormalities (polyp, hyperplasia, submucous myoma) in repeated uterine hysteroscopy after two implantation failures in IVF (13). Operative hysteroscopy showed to be effective in the treatment of intra-uterine adhesions with infertility in Kdous study with good results in achieving pregnancy (24).
Pabuccu et al observed quite an improvement in access to the endometrial cavity during ET procedure after the hysteroscopic shaving procedure in patients with difficult ETs and failed IVFs attempts due to cervical stenosis (25). We treated the structural abnormalities at the time of hysteroscopy and we had no early or late, major or even minor complications in our series. The pathological reports confirmed the observed lesions in 94.7% comparable to the results of Woolcott study (26).
Dicker study showed, that in elderly women, age-related uterine pathology such as submucous myoma, endometrial hyperplasia, and polyps were more prominent, while in younger patients other uterine lesions such as adhesions and tubal ostia occlusion were more common (15). In our experiences, we have seen single polyp and endometrial hyperplasia more in the patients with ≥30years olds rather than the younger group (p- value= 0.78). Also there were more abnormalities especially single polyp, polypoid endometrium and also endometrial hyperplasia in group of the patient with more than 8 years infertility (p-values: 0.08, 0.6, and 0.12, respectively).
According to the result of our study, treatment of the endometrial pathology resulted 34.8% pregnancy rate in the subsequent IVF/ICSI-ET, which is more than the results of Golan (22%) (7), Mihaila (16.6) (19) and Schiano (22%) (13) .This difference seems to be attributed to the exclusion all other factor related to IVF failure, which limited performing hysteroscopy with best result just in patients with endometrial pathology.
Conclusion
TVS showed as a noninvasive, specific but not sensitive method for detecting intracavitary pathology. Hysteroscopy proved to be a very useful, accurate and safe method of assessing and treatment of uterine and endometrial pathologies in patients with repeated IVF/ICSI-ET failures after excluding other possible reason for implantation failure, although it couldn’t evaluate uterine and endometrial functional status.
Acknowledgment
The author wishes to thank the staff of Avesina Infertility Center especially Dr. Akhondi and Dr. Modaberi for their cooperation.
Type of Study: Original Article |
References
1. Margalioth EJ, Ben -Chetrit A, Gal M, Eldar Geva T. Investigation and treatment of repeated implantation failure following IVF-ET. Hum Reprod 2006; 21: 3036-3043. [DOI:10.1093/humrep/del305]
2. Putowski L, Darmochwal-Kolarz D, Rolinski J,Oleszczuk J, Jakowicki J. The immunological profile in infertile women after repeated IVF failures (preliminary study). Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2004; 112: 192-196. [DOI:10.1016/j.ejogrb.2003.06.012]
3. Azem F, Many A, Ben Ami I, Yovel I, Amit A, Lessing JB, et al. Increased rate of thrombophilia in women with repeated IVF failure. Hum Reprod 2004; 19: 368-370. [DOI:10.1093/humrep/deh069]
4. Laird SM, Tuckerman EM, Li TC. Cytokine expression in the endometrium of women with implantation failure and recurrent abortion. Reprod Biomed Online 2006; 13: 13-23. [DOI:10.1016/S1472-6483(10)62011-1]
5. Raziel A, Friedler S, Schachter M, Kasterstein E, Strassburger D, Ron-El R. Increased frequency of female partner chromosomal abnormalities in patients with high order implantation failure after in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril 2002; 78: 515-519. [DOI:10.1016/S0015-0282(02)03298-3]
6. Stern C, Pertile M, Norris H, Hale L, Baker HW. Chromosomal translocations in couples with in vitro fertilization implantation failure. Hum Reprod 1999; 14: 2097-2101 [DOI:10.1093/humrep/14.8.2097]
7. Golan A, Ron-El R, Herman A, Soffer Y, Bukovsky I, Caspi E. Diagnostic hysteroscopy: its value in an in-vitro fertilization/embryo transfer unit. Hum Reprod 1992; 7:1433-1434. [DOI:10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a137589]
8. Shalev J, Meizner I, Bar-Hava I, Dicker D, Mashiach R, Ben-Rafael Z. Predictive value of transvaginal sonography performed before routine diagnostic hysteroscopy for evaluation of infertility. Fertil Steril 2000; 73: 412-417. [DOI:10.1016/S0015-0282(99)00533-6]
9. Hauge K, Flo K, Riedhart M, Granberg S. Can ultrasound -based investigations replace laparascopy and hysteroscopy in infertility? Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2000; 92:167-170. [DOI:10.1016/S0301-2115(00)00442-5]
10. de Kroon CD, de bock GH, Dieben SW, Jansen FW. Saline hysterosonography in abnormal uterine bleeding: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BJOG 2003; 110: 938-947. [DOI:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2003.02472.x]
11. Kelekci S, Kaya E, Alan M, Alan Y, Bilge U, Mollamahmutoglu L. Comparison of transvaginal sonography, saline infusion sonography, and office hysteroscopyin Reproductive- aged women with or without abnormal uterine bleeding. Fertil Steril 2005; 84: 682-686. [DOI:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2005.03.036]
12. Rogerson L, Bates J, Weston M, Duffy S. A comparison of outpatients hysteroscopy with saline infusion hysterosonography. BJOG 2002; 109:800-804. [DOI:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2002.01478.x]
13. Schiano A, Jourdain O, Papaxanthos A, Hocke C, Horovitz J, Dallay D. The value of hysteroscopy after repeated implantation failures with in vitro fertilization. Contracept Fertil Sex 1999; 27: 129-132.
14. Noyes N. Hysteroscopic cervical canal shaving: A new therapy for cervical stenosis before embryo transfer in patients undergoing in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril 1999; 71: 965-966. [DOI:10.1016/S0015-0282(99)00097-7]
15. Dicker D, Ashkenazi J, Feldberg D, Farhi J, Shalev J, Ben-Rafael Z. The value of repeat hysteroscopic evaluation in patients with in vitro fertilization transfer cycles. Fertil Steril 1992; 58: 833-835. [DOI:10.1016/S0015-0282(16)55338-2]
16. Makris N, Xygakis A, Michalas S, Dachlythras M, Prevedourakis C. Day clinic diagnostic hysteroscopy in a state hospital. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 1999; 26:91-92.
17. Alborzi S, Dehbashi S, Khodaee R. Sonohysterosal-pingographic screening for infertile patients. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2003; 82(1): 57-62. [DOI:10.1016/S0020-7292(02)00417-4]
18. Alborzi S, Parsanezhad ME, Mahmoodian N, Alborzi S, Alborzi M . Sonohysterography versus transvaginal Sonography for screening of patients with abnormal uterine bleeding. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2007; 96: 20-23. [DOI:10.1016/j.ijgo.2006.09.004]
19. diagnosis and treatment of infertility. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi 2005; 109: 537-541.
20. Mihaila C, Anton E. Significance of hysteroscopy in the Ragni G, Diaferia D, Vegetti W, Colombo M, Arnoldi M, Crosignani PG. Effectiveness of sonohysteroscopy in infertile patient workshop: a comparison with transvaginal ultrasonography and hysteroscopy. Gynecol Obstet Invest 2005; 59:184-188. [DOI:10.1159/000084294]
21. Faghali J, Bakar J, Mayenga JM, Ségard L, Hamou J, Driguez P, et al. Systematic hysteroscopy prior to in vitro fertilization. Gynecol Obstet Fertil 2003; 31: 127-131. [DOI:10.1016/S1297-9589(03)00007-9]
22. La Sala GB, Montanari R, Dessanti L , Cigarini C, Sartori F. The role of diagnostic hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy in assisted reproductive endocrinologies. Fertil Steril 1998; 70:378-380. [DOI:10.1016/S0015-0282(98)00147-2]
23. Oliveria FG, Abdelmassih VG, Diamond MP, Dozortsev D, Nagy ZP, Abdelmassih R. Uterine cavity findings and hysteroscopic interventions in patients undergoing in vitro fertilization -embryo transfer who repeatedly cannot conceive. Fertil Steril 2003; 80: 1371-1375. [DOI:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2003.05.003]
24. Kdous M, Hachicha R, Zhiou F, Ferchiou M, Chaker A, Meriah S. Fertility after hysteroscopic treatment of intra-uterine adhesions. Gynecol Obstet Fertil 2003; 31: 422-428. [DOI:10.1016/S1297-9589(03)00101-2]
25. Pabuccu R, Ceyhan ST , Onalan G, Goktolga U, Ercan CM, Selam B. Successful treatment of cervical stenosis with hysteroscopic canalization before embryo transfer in patients undergoing IVF: A case series. J Minimum Invasive Gynecol 2005; 12: 436-438. [DOI:10.1016/j.jmig.2005.06.003]
26. Woolcott R, Petchpud A. The efficacy of hysteroscopy: a comparison of women presenting with infertility versus other gynaecological symptoms. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1996; 36: 226-227.
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |


