Mon, Feb 23, 2026
[Archive]
Volume 23, Issue 1 (January 2025)
IJRM 2025, 23(1): 79-90 |
Back to browse issues page
Ethics code: IR.IAU.AMOL.REC.1400.019
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Mohebbi Kian E, Barancheshmeh M, Najafzadehvarzi H, Ghoreishi S M, Shokrzadeh N. Therapeutic potential of fennel essential oil and manganese in modulating steroidal hormonal imbalance and ovarian alterations in rats with polycystic ovarian syndrome: An experimental study. IJRM 2025; 23 (1) :79-90
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-3188-en.html
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-3188-en.html
Ensiyeh Mohebbi Kian1 

 , Maryam Barancheshmeh1
, Maryam Barancheshmeh1 

 , Hossein Najafzadehvarzi *2
, Hossein Najafzadehvarzi *2 

 , Seyedeh Masoumeh Ghoreishi3
, Seyedeh Masoumeh Ghoreishi3 

 , Naser Shokrzadeh4
, Naser Shokrzadeh4 




 , Maryam Barancheshmeh1
, Maryam Barancheshmeh1 

 , Hossein Najafzadehvarzi *2
, Hossein Najafzadehvarzi *2 

 , Seyedeh Masoumeh Ghoreishi3
, Seyedeh Masoumeh Ghoreishi3 

 , Naser Shokrzadeh4
, Naser Shokrzadeh4 


1- Department of Pharmacy, Ayatollah Amoli Branch, Islamic Azad University, Amol, Iran.
2- Pharmacology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Babol University of Medical Sciences, Babol, Iran. & Cellular and Molecular Biology Research Center, Health Research Institute, Babol University of Medical Sciences, Babol, Iran. ,Najafzadehvarzi@gmail.com
3- Cellular and Molecular Biology Research Center, Health Research Institute, Babol University of Medical Sciences, Babol, Iran.
4- Reproductive Health Research Center, Clinical Research Institute, Urmia University of Medical Sciences, Urmia, Iran.
2- Pharmacology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Babol University of Medical Sciences, Babol, Iran. & Cellular and Molecular Biology Research Center, Health Research Institute, Babol University of Medical Sciences, Babol, Iran. ,
3- Cellular and Molecular Biology Research Center, Health Research Institute, Babol University of Medical Sciences, Babol, Iran.
4- Reproductive Health Research Center, Clinical Research Institute, Urmia University of Medical Sciences, Urmia, Iran.
Abstract: (993 Views)
Background: Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a prevalent hormonal disorder among women of reproductive age, resulting in female infertility. Researchers are exploring safe and affordable treatments for this disorder.
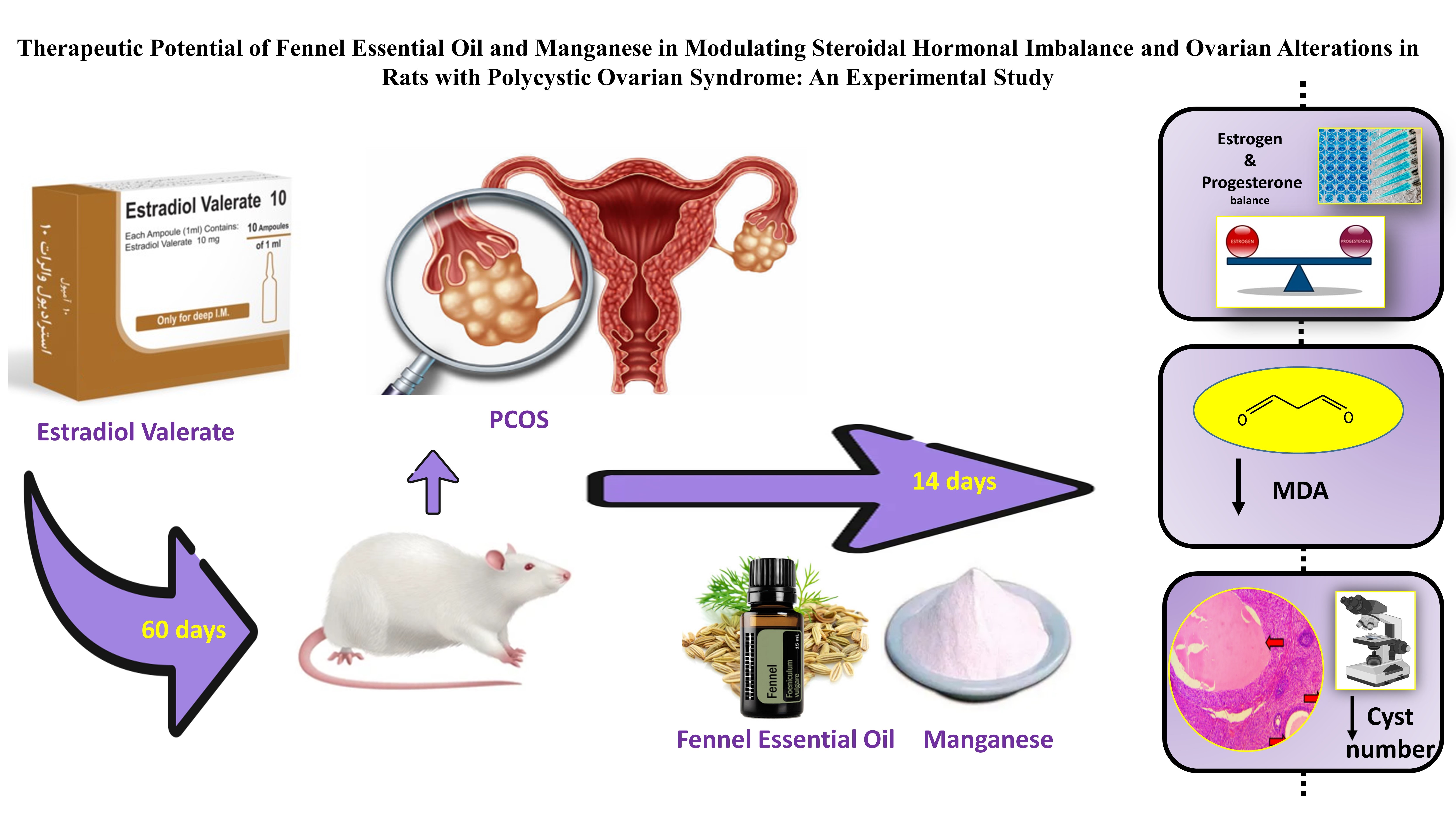
Objective: This study explored the therapeutic effects of fennel essential oil (FEO) and manganese (Mn) on hormonal and histological markers in rats with estradiol valerate-induced PCOS.
Materials and Methods: In this experimental study, 35 adult female Wistar rats (9 wk old, 200-250 gr) were divided into 7 groups. For 14 days, groups 1-4 received normal saline intraperitoneally, sesame oil intramuscularly, FEO intraperitoneally, and Mn orally, respectively. PCOS was induced in remaining groups through a single intramuscular injection of estradiol valerate. 60 days after induction, the 6th and 7th groups were treated individually with intraperitoneal FEO and oral Mn for 14 days. Blood samples were analyzed for estrogen, progesterone, and malondialdehyde (MDA) markers. The ovarian tissues were histologically examined to assess cyst formation and structural changes.
Results: FEO significantly increased estrogen and progesterone levels in PCOS rats compared to the PCOS group (p ≤ 0.05). Mn also elevated progesterone levels, but the change was not statistically significant (p > 0.05). No significant differences in MDA levels were observed between the PCOS and PCOS+FEO groups. Although MDA levels decreased in the PCOS+Mn group, the reduction was not statistically significant (p > 0.05). Both FEO and Mn treatments significantly reduced ovarian cyst numbers compared to untreated PCOS rats (p ≤ 0.05).
Conclusion: FEO and Mn demonstrated potential in restoring hormonal balance and improving ovarian histology, offering promise as low-cost treatments for PCOS.
Objective: This study explored the therapeutic effects of fennel essential oil (FEO) and manganese (Mn) on hormonal and histological markers in rats with estradiol valerate-induced PCOS.
Materials and Methods: In this experimental study, 35 adult female Wistar rats (9 wk old, 200-250 gr) were divided into 7 groups. For 14 days, groups 1-4 received normal saline intraperitoneally, sesame oil intramuscularly, FEO intraperitoneally, and Mn orally, respectively. PCOS was induced in remaining groups through a single intramuscular injection of estradiol valerate. 60 days after induction, the 6th and 7th groups were treated individually with intraperitoneal FEO and oral Mn for 14 days. Blood samples were analyzed for estrogen, progesterone, and malondialdehyde (MDA) markers. The ovarian tissues were histologically examined to assess cyst formation and structural changes.
Results: FEO significantly increased estrogen and progesterone levels in PCOS rats compared to the PCOS group (p ≤ 0.05). Mn also elevated progesterone levels, but the change was not statistically significant (p > 0.05). No significant differences in MDA levels were observed between the PCOS and PCOS+FEO groups. Although MDA levels decreased in the PCOS+Mn group, the reduction was not statistically significant (p > 0.05). Both FEO and Mn treatments significantly reduced ovarian cyst numbers compared to untreated PCOS rats (p ≤ 0.05).
Conclusion: FEO and Mn demonstrated potential in restoring hormonal balance and improving ovarian histology, offering promise as low-cost treatments for PCOS.
This article has been extracted from Pharm. D. Thesis. (Ensiyeh Mohebbi Kian)
Type of Study: Original Article |
Subject:
Reproductive Endocrinology
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |