Thu, Feb 19, 2026
[Archive]
Volume 22, Issue 7 (July 2024)
IJRM 2024, 22(7): 527-538 |
Back to browse issues page
Ethics code: IR.QUMS.REC.1398.165
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Chegini R, Sadeghi M, Shirian S, Sabbaghziarani F, Aali E, Soleimani P, et al . Effects of combination of melatonin and L-carnitine on in vitro maturation in mouse oocytes: An experimental study. IJRM 2024; 22 (7) :527-538
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-3240-en.html
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-3240-en.html
Raziye Chegini1 

 , Morteza Sadeghi2
, Morteza Sadeghi2 

 , Sadegh Shirian3
, Sadegh Shirian3 

 , Fatemeh Sabbaghziarani4
, Fatemeh Sabbaghziarani4 

 , Ehsan Aali5
, Ehsan Aali5 

 , Pouriya Soleimani6
, Pouriya Soleimani6 

 , Mohammad Reza Ashtari Majelan5
, Mohammad Reza Ashtari Majelan5 

 , Fariba Zafari *7
, Fariba Zafari *7 

 , Shahram Darabi5
, Shahram Darabi5 




 , Morteza Sadeghi2
, Morteza Sadeghi2 

 , Sadegh Shirian3
, Sadegh Shirian3 

 , Fatemeh Sabbaghziarani4
, Fatemeh Sabbaghziarani4 

 , Ehsan Aali5
, Ehsan Aali5 

 , Pouriya Soleimani6
, Pouriya Soleimani6 

 , Mohammad Reza Ashtari Majelan5
, Mohammad Reza Ashtari Majelan5 

 , Fariba Zafari *7
, Fariba Zafari *7 

 , Shahram Darabi5
, Shahram Darabi5 


1- Department of Anatomical Sciences, School of Medicine, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
2- Human Genetic Research Center, Baqiyatallah University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
3- Department of Pathology, School of Veterinary Medicine, Shahrekord University, Shahrekord, Iran. & Shiraz Molecular Pathology Research Center, Dr. Daneshbod Path Lab, Shiraz, Iran.
4- Cellular and Molecular Research Center, Research Institute for Prevention of Non-communicable Disease, Qazvin University of Medical Sciences, Qazvin, Iran. & Shiraz Molecular Pathology Research Center, Dr. Daneshbod Path Lab, Shiraz, Iran.
5- Cellular and Molecular Research Center, Research Institute for Prevention of Non-communicable Disease, Qazvin University of Medical Sciences, Qazvin, Iran.
6- Department of Nursing, Faculty of Nursing and Midwifery, Qazvin University of Medical Sciences, Qazvin, Iran.
7- Cellular and Molecular Research Center, Research Institute for Prevention of Non-communicable Disease, Qazvin University of Medical Sciences, Qazvin, Iran. ,f.zafari@qums.ac.ir
2- Human Genetic Research Center, Baqiyatallah University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
3- Department of Pathology, School of Veterinary Medicine, Shahrekord University, Shahrekord, Iran. & Shiraz Molecular Pathology Research Center, Dr. Daneshbod Path Lab, Shiraz, Iran.
4- Cellular and Molecular Research Center, Research Institute for Prevention of Non-communicable Disease, Qazvin University of Medical Sciences, Qazvin, Iran. & Shiraz Molecular Pathology Research Center, Dr. Daneshbod Path Lab, Shiraz, Iran.
5- Cellular and Molecular Research Center, Research Institute for Prevention of Non-communicable Disease, Qazvin University of Medical Sciences, Qazvin, Iran.
6- Department of Nursing, Faculty of Nursing and Midwifery, Qazvin University of Medical Sciences, Qazvin, Iran.
7- Cellular and Molecular Research Center, Research Institute for Prevention of Non-communicable Disease, Qazvin University of Medical Sciences, Qazvin, Iran. ,
Abstract: (1457 Views)
Background: Melatonin and L-carnitine are free radical scavengers with antiapoptotic and antioxidant properties that improve oocyte development.
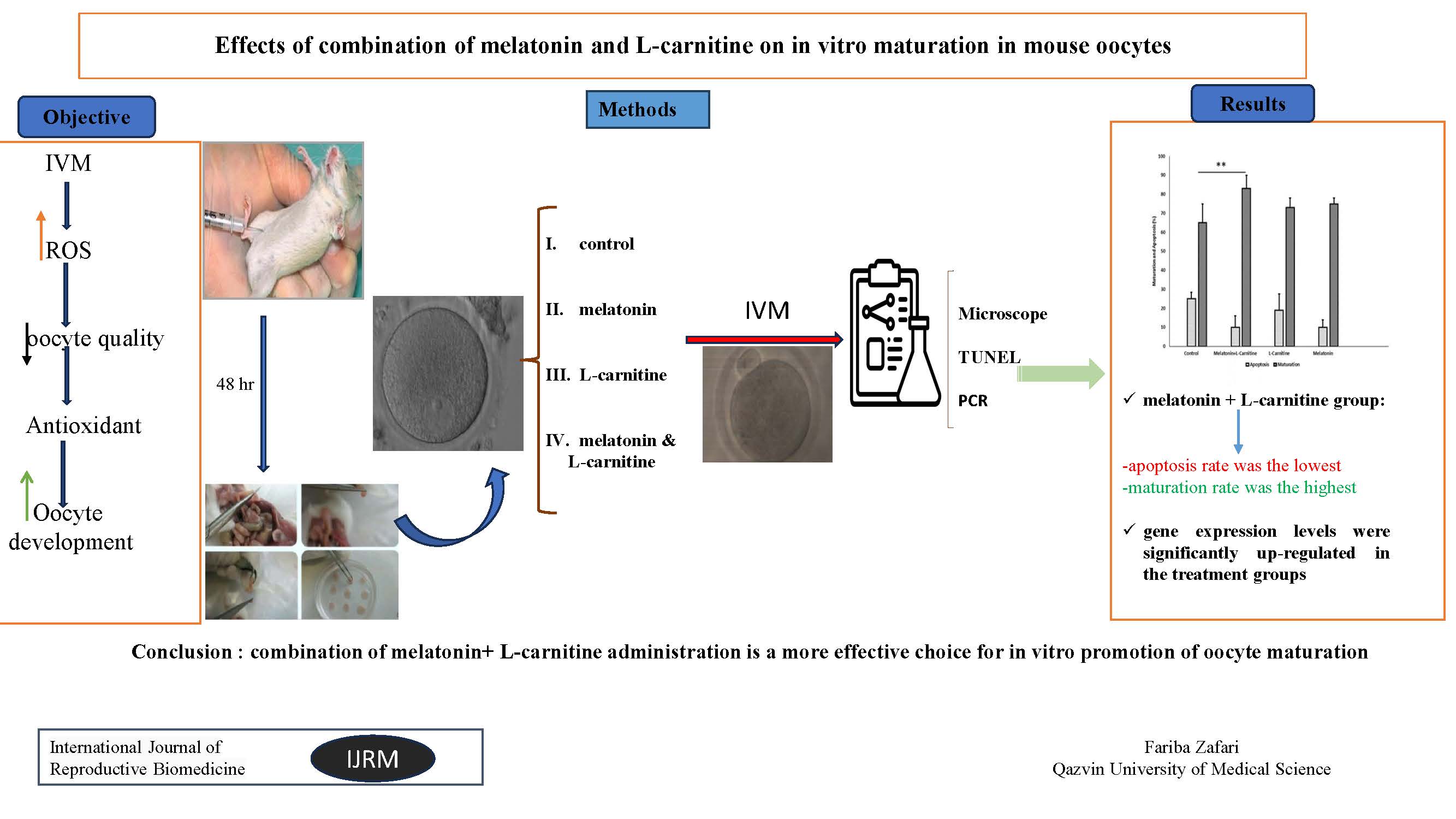
Objective: This study aimed to find the possible effect of combining 2 antioxidant agents of melatonin and L-carnitine on oocyte morphology, maturation, apoptosis, and expression of bone morphogenetic protein 15 (BMP-15) and growth differentiation factor 9 (GDF-9) genes in a mice model.
Materials and Methods: To overstimulation, 60 female NMRI mice were injected intraperitoneally using mare serum gonadotropin. On day 2 post-injection, 70 cumulus-oocyte complexes were collected from each mouse. The collected oocytes randomly were then divided into 4 groups including, the control, melatonin, L-carnitine, melatonin + L-carnitine groups. The morphology and maturation rate of the oocytes was evaluated using a light microscope. Apoptosis was identified by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling assay and the expression of BMP-15 and growth and differentiation factor GDF-9 genes was also evaluated by real-time polymerase chain reaction.
Results: Oocyte diameter significantly was increased in combination treatment of L-carnitine and melatonin compared to other groups (p < 0.05). L-carnitine group showed the highest mean percentage of oocyte cytoplasmic pattern. Results of the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling indicated that the lowest apoptosis rate belonged to the melatonin + L-carnitine group. Moreover, the combination groups showed the highest number of oocytes and maturation rate. The BMP-15 and GDF-9 genes were significantly upregulated in all treatment groups compared to the control group.
Conclusion: Our results suggested a combination of melatonin + L-carnitine administration as a more effective choice for in vitro promotion of oocyte maturation.
Objective: This study aimed to find the possible effect of combining 2 antioxidant agents of melatonin and L-carnitine on oocyte morphology, maturation, apoptosis, and expression of bone morphogenetic protein 15 (BMP-15) and growth differentiation factor 9 (GDF-9) genes in a mice model.
Materials and Methods: To overstimulation, 60 female NMRI mice were injected intraperitoneally using mare serum gonadotropin. On day 2 post-injection, 70 cumulus-oocyte complexes were collected from each mouse. The collected oocytes randomly were then divided into 4 groups including, the control, melatonin, L-carnitine, melatonin + L-carnitine groups. The morphology and maturation rate of the oocytes was evaluated using a light microscope. Apoptosis was identified by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling assay and the expression of BMP-15 and growth and differentiation factor GDF-9 genes was also evaluated by real-time polymerase chain reaction.
Results: Oocyte diameter significantly was increased in combination treatment of L-carnitine and melatonin compared to other groups (p < 0.05). L-carnitine group showed the highest mean percentage of oocyte cytoplasmic pattern. Results of the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling indicated that the lowest apoptosis rate belonged to the melatonin + L-carnitine group. Moreover, the combination groups showed the highest number of oocytes and maturation rate. The BMP-15 and GDF-9 genes were significantly upregulated in all treatment groups compared to the control group.
Conclusion: Our results suggested a combination of melatonin + L-carnitine administration as a more effective choice for in vitro promotion of oocyte maturation.
Type of Study: Original Article |
Subject:
Assisted Reproductive Technologies
References
1. Yalçınkaya E, Calışkan E, Budak O. In vitro maturation may prevent the cancellation of in vitro fertilization cycles in poor responder patients: A case report. J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc 2013; 14: 235-237. [DOI:10.5152/jtgga.2013.68335] [PMID] [PMCID]
2. De Vos M, Grynberg M, Ho TM, Yuan Y, Albertini DF, Gilchrist RB. Perspectives on the development and future of oocyte IVM in clinical practice. J Assist Reprod Genet 2021; 38: 1265-1280. [DOI:10.1007/s10815-021-02263-5] [PMID] [PMCID]
3. Li W, Cheng K, Zhang Y, Meng Q, Zhu Se, Zhou G. No effect of exogenous melatonin on development of cryopreserved metaphase II oocytes in mouse. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 2015; 6: 42. [DOI:10.1186/s40104-015-0041-0] [PMID] [PMCID]
4. Budani MC, Tiboni GM. Effects of supplementation with natural antioxidants on oocytes and preimplantation embryos. Antioxidants 2020; 9: 612. [DOI:10.3390/antiox9070612] [PMID] [PMCID]
5. Belli M, Shimasaki S. Molecular aspects and clinical relevance of GDF9 and BMP15 in ovarian function. Vitam Horm 2018; 107: 317-348. [DOI:10.1016/bs.vh.2017.12.003] [PMID] [PMCID]
6. Sanfins A, Rodrigues P, Albertini DF. GDF-9 and BMP-15 direct the follicle symphony. J Assist Reprod Genet 2018; 35: 1741-1750. [DOI:10.1007/s10815-018-1268-4] [PMID] [PMCID]
7. Mortezaee K, Sabbaghziarani F, Omidi A, Dehpour AR, Omidi N, Ghasemi S, et al. Therapeutic value of melatonin post-treatment on CCl(4)-induced fibrotic rat liver. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2016; 94: 119-130. [DOI:10.1139/cjpp-2015-0266] [PMID]
8. Loren P, Sánchez R, Arias ME, Felmer R, Risopatrón J, Cheuquemán C. Melatonin scavenger properties against oxidative and nitrosative stress: Impact on gamete handling and in vitro embryo production in humans and other mammals. Int J Mol Sci 2017; 18: 1119. [DOI:10.3390/ijms18061119] [PMID] [PMCID]
9. Zare Z, Masteri Farahani R, Salehi M, Piryaei A, Ghaffari Novin M, Fadaei Fathabadi F, et al. Effect of L-carnitine supplementation on maturation and early embryo development of immature mouse oocytes selected by brilliant cresyle blue staining. J Assist Reprod Genet 2015; 32: 635-643. [DOI:10.1007/s10815-015-0430-5] [PMID] [PMCID]
10. Li J, Liu L, Weng J, Yin TL, Yang J, Feng HL. Biological roles of l-carnitine in oocyte and early embryo development. Mol Reprod Dev 2021; 88: 673-685. [DOI:10.1002/mrd.23542] [PMID]
11. Gong X, Shen L, Zhang H, Ai J, Gilchrist RB, Zhao Y. CAPA-IVM improves the cytoplasmic quality of in vitro-matured oocytes from unstimulated mice. Theriogenology 2023; 212: 117-128. [DOI:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2023.09.004] [PMID]
12. Tadayoni S, Malekzadeh Shafarodi M, Ghasemi Hamidabadi H, Esmailnejad Moghaddam A, Khalilian A, Rezaei N. [Effect of combination of melatonin and all-trans retinoic acid on maturation, fertilization and embryonic development of immature mouse oocytes]. J Gorgan Univ Med Sci 2015; 17: 46-54. (in Persian)
13. Moawad AR, Salama A, Badr MR, Fathi M. Beneficial effects of L-carnitine supplementation during IVM of canine oocytes on their nuclear maturation and development in vitro. Animals 2021; 11: 581. [DOI:10.3390/ani11020581] [PMID] [PMCID]
14. Lazzaroni-Tealdi E, Barad DH, Albertini DF, Yu Y, Kushnir VA, Russell H, et al. Oocyte scoring enhances embryo-scoring in predicting pregnancy chances with IVF where it counts most. PloS One 2015; 10: e0143632. [DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0143632] [PMID] [PMCID]
15. Xu HY, Yang XG, Lu SS, Liang XW, Lu YQ, Zhang M, et al. Treatment with acetyl-l-carnitine during in vitro maturation of buffalo oocytes improves oocyte quality and subsequent embryonic development. Theriogenology 2018; 118: 80-89. [DOI:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2018.05.033] [PMID]
16. Gupta S, Sekhon L, Kim Y, Agarwal A. The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in assisted reproduction. Current Women's Health Reviews 2010; 6: 227-238. [DOI:10.2174/157340410792007046]
17. Zhao XM, Wang N, Hao HS, Li CY, Zhao YH, Yan CL, et al. Melatonin improves the fertilization capacity and developmental ability of bovine oocytes by regulating cytoplasmic maturation events. J Pineal Res 2018; 64: e12455. [DOI:10.1111/jpi.12445] [PMID]
18. Kalehoei E, Moradi M, Azadbakht M, Zhaleh H, Parvini M, Cheraghbaeigi S, et al. In vitro maturation medium supplementation: Utilization of repaglinide, L-carnitine, and mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium to improve developmental competence of oocytes derived from endometriosis mouse models. Braz J Med Biol Res 2022; 55: e11948. [DOI:10.1590/1414-431x2022e11948] [PMID] [PMCID]
19. Shi XY, Jin XH, Lin JY, Sun LZ, Liu X, Zhang TY, et al. Idebenone relieves the damage of heat stress on the maturation and developmental competence of porcine oocytes. Reprod Domest Anim 2022; 57: 418-428. [DOI:10.1111/rda.14080] [PMID]
20. Cadenas J, Pors SE, Kumar A, Kalra B, Kristensen SG, Andersen CY, et al. Concentrations of oocyte secreted GDF9 and BMP15 decrease with MII transition during human IVM. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2022; 20: 126. [DOI:10.1186/s12958-022-01000-6] [PMID] [PMCID]
21. Farahavar A, Shahne A, Kohram H, Vahedi V. Effect of melatonin on in vitro maturation of bovine oocytes. Afr J Biotechnol 2010; 9: 2579-2583.
22. Dunning KR, Robker RL. The role of L-carnitine during oocyte in vitro maturation: Essential co-factor? Proceedings of the 31st Annual Meeting of the Brazilian Embryo Technology Society (SBTE); 2017 August 17-19; Brazil. Anim Reprod 2017; 14: 469-475. [DOI:10.21451/1984-3143-AR988]
23. Voiculescu SE, Zygouropoulos N, Zahiu CD, Zagrean AM. Role of melatonin in embryo fetal development. J Med Life 2014; 7: 488-492.
24. He B, Yin C, Gong Y, Liu J, Guo H, Zhao R. Melatonin-induced increase of lipid droplets accumulation and in vitro maturation in porcine oocytes is mediated by mitochondrial quiescence. J Cell Pysiolo 2018; 233: 302-312. [DOI:10.1002/jcp.25876] [PMID]
25. Sprícigo JF, Morató R, Arcarons N, Yeste M, Dode MA, López-Bejar M, et al. Assessment of the effect of adding L-carnitine and/or resveratrol to maturation medium before vitrification on in vitro-matured calf oocytes. Theriogenology 2017; 89: 47-57. [DOI:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2016.09.035] [PMID]
26. Lin T, Lee J, Kang J, Kim S, Zhang J. The influence and role of melatonin on in vitro oocyte maturation and embryonic development in pig and cattle. Korean J Agr Sci 2017; 44: 309-317. [DOI:10.7744/kjoas.20170050]
27. Mortezaee K, Pasbakhsh P, Kashani I, Sabbaghziarani F, Omidi A, Zendedel A, et al. Melatonin pretreatment enhances the homing of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells following transplantation in a rat model of liver fibrosis. Iran Biomed J 2016; 20: 207-216.
28. Rodrigues-Cunha MC, Mesquita LG, Bressan F, Collado MD, Balieiro JC, Schwarz KR, et al. Effects of melatonin during IVM in defined medium on oocyte meiosis, oxidative stress, and subsequent embryo development. Theriogenology 2016; 86: 1685-1694. [DOI:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2016.05.026] [PMID]
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |