Sun, Feb 22, 2026
[Archive]
Volume 22, Issue 10 (October 2024)
IJRM 2024, 22(10): 821-836 |
Back to browse issues page
Ethics code: IR.TUMS.AEC.1401.122
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Esfehani R, Khadivi F, Valipour J, Shabani M, Ramesh M, Javanbakht P, et al . Secretome of human amniotic membrane stem cells promote recovery and testicular functions through modulating SIRT1/NRF2/TNF-α pathway in mice testicular torsion: An experimental study. IJRM 2024; 22 (10) :821-836
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-3292-en.html
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-3292-en.html
Roghayeh Esfehani1 

 , Farnaz Khadivi2
, Farnaz Khadivi2 

 , Jamal Valipour1
, Jamal Valipour1 

 , Maryam Shabani3
, Maryam Shabani3 

 , Mahya Ramesh1
, Mahya Ramesh1 

 , Parinaz Javanbakht1
, Parinaz Javanbakht1 

 , Davood Zarini1
, Davood Zarini1 

 , Sina Mojaverrostami *4
, Sina Mojaverrostami *4 

 , Masih Hoseini5
, Masih Hoseini5 




 , Farnaz Khadivi2
, Farnaz Khadivi2 

 , Jamal Valipour1
, Jamal Valipour1 

 , Maryam Shabani3
, Maryam Shabani3 

 , Mahya Ramesh1
, Mahya Ramesh1 

 , Parinaz Javanbakht1
, Parinaz Javanbakht1 

 , Davood Zarini1
, Davood Zarini1 

 , Sina Mojaverrostami *4
, Sina Mojaverrostami *4 

 , Masih Hoseini5
, Masih Hoseini5 


1- Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
2- Medical Plants Research Center, Basic Health Sciences Institute, Shahrekord University of Medical Sciences, Shahrekord, Iran. & Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine, Shahrekord University of Medical Sciences, Shahrekord, Iran.
3- Department of Clinical Biochemistry, School of Medicine, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
4- Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. ,smojaver@sina.tums.ac.ir
5- Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine, Shahrekord University of Medical Sciences, Shahrekord, Iran.
2- Medical Plants Research Center, Basic Health Sciences Institute, Shahrekord University of Medical Sciences, Shahrekord, Iran. & Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine, Shahrekord University of Medical Sciences, Shahrekord, Iran.
3- Department of Clinical Biochemistry, School of Medicine, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
4- Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. ,
5- Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine, Shahrekord University of Medical Sciences, Shahrekord, Iran.
Abstract: (1156 Views)
Background: Testicular ischemia/reperfusion injury, a significant result of testicular torsion, can lead to the risk of male infertility.
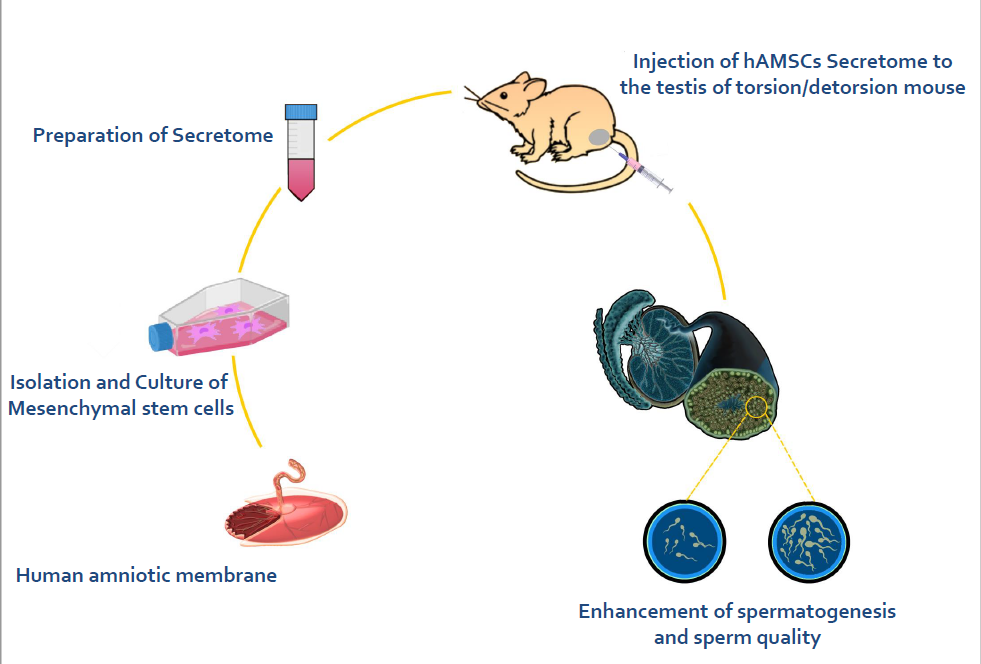
Objective: The current study aimed to evaluate the effect of human amniotic membrane-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hAMSCs) secretome on testicular torsion/detorsion (T/D) in mice.
Materials and Methods: All the experiments were performed in the Anatomy Department of Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran, during the period of March 2023 to December 2023. 40 male NMRI mice (5-7 wk, 25-30 gr) were randomized into: 1) the sham group: mice received sham operations with no other interventions, 2) T/D group, 3) negative control group; torsion detorsion + intratesticular injection of Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium/Nutrient Mixture F-12, and 4) the T/D group + hAMSCs secreted factors. Serum testosterone levels, hematoxylin and eosin staining, and sperm quality parameters were used to evaluate the therapeutic effects of hAMSCs secreted factors on the testicular structure and function. Tissue oxidative stress was measured by determining malondialdehyde, superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase-1. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1, NAD-dependent deacetylase sirtuin-1, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and tumor protein P53 mRNA expressions were assessed in testis via real-time polymerase chain reaction.
Results: The results showed that hAMSCs secreted factors alleviated testicular T/D injury by attenuating oxidative stress, inflammatory response, and apoptosis via modulating the sirtuin-1/ nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2/tumor necrosis factor-alpha signaling pathway.
Conclusion: hAMSCs secreted factors increased antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic properties which consequently increased testosterone levels, spermatogenesis, and sperm quality parameters.
Objective: The current study aimed to evaluate the effect of human amniotic membrane-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hAMSCs) secretome on testicular torsion/detorsion (T/D) in mice.
Materials and Methods: All the experiments were performed in the Anatomy Department of Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran, during the period of March 2023 to December 2023. 40 male NMRI mice (5-7 wk, 25-30 gr) were randomized into: 1) the sham group: mice received sham operations with no other interventions, 2) T/D group, 3) negative control group; torsion detorsion + intratesticular injection of Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium/Nutrient Mixture F-12, and 4) the T/D group + hAMSCs secreted factors. Serum testosterone levels, hematoxylin and eosin staining, and sperm quality parameters were used to evaluate the therapeutic effects of hAMSCs secreted factors on the testicular structure and function. Tissue oxidative stress was measured by determining malondialdehyde, superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase-1. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1, NAD-dependent deacetylase sirtuin-1, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and tumor protein P53 mRNA expressions were assessed in testis via real-time polymerase chain reaction.
Results: The results showed that hAMSCs secreted factors alleviated testicular T/D injury by attenuating oxidative stress, inflammatory response, and apoptosis via modulating the sirtuin-1/ nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2/tumor necrosis factor-alpha signaling pathway.
Conclusion: hAMSCs secreted factors increased antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic properties which consequently increased testosterone levels, spermatogenesis, and sperm quality parameters.
Type of Study: Original Article |
Subject:
Reproductive Anatomy
References
1. Yousefi-Manesh H, Shirooie S, Hemati S, Shokrian-Zeini M, Zarei N, Raoufi M, et al. Protective effects of modafinil administration on testicular torsion/detorsion damage in rats. Exp Mol Pathol 2019; 111: 104305. [DOI:10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.104305] [PMID]
2. Akhigbe R, Hamed M, Odetayo A, Akhigbe T, Ajayi A, Ajibogun F. Omega-3 fatty acid rescues ischaemia/perfusion-induced testicular and sperm damage via modulation of lactate transport and xanthine oxidase/uric acid signaling. Biomed Pharmacother 2021; 142: 111975. [DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111975] [PMID]
3. Jafari A, Ghasemnejad-Berenji H, Nemati M, Ghasemnejad-Berenji M. Topiramate: A novel protective agent against ischemia reperfusion-induced oxidative injury after testicular torsion/detorsion. Am J Emerg Med 2021; 44: 257-261. [DOI:10.1016/j.ajem.2020.03.060] [PMID]
4. Vickers NJ. Animal communication: When I'm calling you, will you answer too? Curr Biol 2017; 27: R713-R715. [DOI:10.1016/j.cub.2017.05.064] [PMID]
5. Cardoso JP, Cocuzza M, Elterman D. Optimizing male fertility: Oxidative stress and the use of antioxidants. World J Urol 2019; 37: 1029-1034. [DOI:10.1007/s00345-019-02656-3] [PMID]
6. Ni Sh, Wang D, Qiu X, Pang L, Song Z, Guo K. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protect against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rat by activating Nrf2 signaling. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015; 8: 7752-7761.
7. Yang L, Shen Zh-Y, Wang R-R, Yin M-L, Zheng W-P, Wu B, et al. Effects of heme oxygenase-1-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on microcirculation and energy metabolism following liver transplantation. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23: 3449. [DOI:10.3748/wjg.v23.i19.3449] [PMID] [PMCID]
8. Ji X, Lu Y, Tian H, Meng X, Wei M, Cho WC. Chemoresistance mechanisms of breast cancer and their countermeasures. Biomed Pharmacother 2019; 114: 108800. [DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108800] [PMID]
9. Ahmed SA, Mohammed WI. Carvedilol induces the antiapoptotic proteins Nrf2 and Bcl2 and inhibits cellular apoptosis in aluminum-induced testicular toxicity in male Wistar rats. Biomed Pharmacother 2021; 139: 111594. [DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111594] [PMID]
10. Abdelzaher WY, Mostafa-Hedeab G, Sayed AboBakr Ali AH, Fawzy MA, Ahmed AF, Bahaa El-deen MA, et al. Idebenone regulates sirt1/Nrf2/TNF-α pathway with inhibition of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in testicular torsion/detorsion in juvenile rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 2022; 41: 09603271221102515. [DOI:10.1177/09603271221102515] [PMID]
11. Munoz-Perez E, Gonzalez-Pujana A, Igartua M, Santos-Vizcaino E, Hernandez RM. Mesenchymal stromal cell secretome for the treatment of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases: Latest trends in isolation, content optimization and delivery avenues. Pharmaceutics 2021; 13: 1802. [DOI:10.3390/pharmaceutics13111802] [PMID] [PMCID]
12. Jiang F, Zhang W, Zhou M, Zhou Z, Shen M, Chen N, et al. Human amniotic mesenchymal stromal cells promote bone regeneration via activating endogenous regeneration. Theranostics 2020; 10: 6216. [DOI:10.7150/thno.45249] [PMID] [PMCID]
13. Liu Q-W, Huang Q-M, Wu H-Y, Zuo G-S-L, Gu H-C, Deng K-Y, et al. Characteristics and therapeutic potential of human amnion-derived stem cells. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 970. [DOI:10.3390/ijms22020970] [PMID] [PMCID]
14. Saheli M, Bayat M, Ganji R, Hendudari F, Kheirjou R, Pakzad M, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells-conditioned medium improves diabetic wound healing mainly through modulating fibroblast behaviors. Arch Dermatol Res 2020; 312: 325-336. [DOI:10.1007/s00403-019-02016-6] [PMID]
15. Stavely R, Nurgali K. The emerging antioxidant paradigm of mesenchymal stem cell therapy. Stem Cells Transl Med 2020; 9: 985-1006. [DOI:10.1002/sctm.19-0446] [PMID] [PMCID]
16. Qamar AY, Hussain T, Rafique MK, Bang S, Tanga BM, Seong G, et al. The role of stem cells and their derived extracellular vesicles in restoring female and male fertility. Cells 2021; 10: 2460. [DOI:10.3390/cells10092460] [PMID] [PMCID]
17. Bader R, Ibrahim J-N, Mourad A, Moussa M, Azoury J, Azoury J, et al. Improvement of human sperm vacuolization and DNA fragmentation co-cultured with adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell secretome: In vitro effect. Int J Stem Cells 2019; 12: 388-399. [DOI:10.15283/ijsc19047] [PMID] [PMCID]
18. Ramesh M, Mojaverrostami S, Khadivi F, Rastegar T, Abbasi Y, Bashiri Z. Protective effects of human amniotic membrane derived mesenchymal stem cells (hAMSCs) secreted factors on mouse spermatogenesis and sperm chromatin condensation following unilateral testicular torsion. Ann Anat 2023; 249: 152084. [DOI:10.1016/j.aanat.2023.152084] [PMID]
19. Abdollahifar M-A, Azad N, Faraji Sani M, Raoofi A, Abdi S, Aliaghaei A, et al. Impaired spermatogenesis caused by busulfan is partially ameliorated by treatment with conditioned medium of adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biotech Histochem 2022; 97: 107-117. [DOI:10.1080/10520295.2021.1905182] [PMID]
20. De León-Ramírez YM, Lara-García M, Pacheco P, Lara-García O, Martínez-Gómez M, Cuevas-Romero E, et al. Histomorphological testicular changes and decrease in the sperm count in pubertal rats induced by a high-sugar diet. Ann Anat 2021; 235: 151678. [DOI:10.1016/j.aanat.2021.151678] [PMID]
21. Ikhlas S, Ahmad M. Acute and sub-acute bisphenol-B exposures adversely affect sperm count and quality in adolescent male mice. Chemosphere 2020; 242: 125286. [DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125286] [PMID]
22. Roy VK, Verma R, Krishna A. Carnitine-mediated antioxidant enzyme activity and Bcl2 expression involves peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α in mouse testis. Reprod Fertil Dev 2017; 29: 1057-1063. [DOI:10.1071/RD15336] [PMID]
23. Qian C, Meng Q, Lu J, Zhang L, Li H, Huang B. Human amnion mesenchymal stem cells restore spermatogenesis in mice with busulfan-induced testis toxicity by inhibiting apoptosis and oxidative stress. Stem Cell Res Ther 2020; 11: 290. [DOI:10.1186/s13287-020-01803-7] [PMID] [PMCID]
24. Fatima S, Alwaznah R, Aljuraiban GS, Wasi S, Abudawood M, Abulmeaty M, et al. Effect of seminal redox status on lipid peroxidation, apoptosis and DNA fragmentation in spermatozoa of infertile Saudi males. Saudi Med J 2020; 41: 238. [DOI:10.15537/smj.2020.3.24975] [PMID] [PMCID]
25. Kazaz IO, Demir S, Kerimoglu G, Colak F, Alemdar NT, Akman AU, et al. Effect of chrysin on endoplasmic reticulum stress in a rat model of testicular torsion. J Invest Surg 2022; 35: 1106-1111. [DOI:10.1080/08941939.2021.2015489] [PMID]
26. Jeddi F, Soozangar N, Sadeghi MR, Somi MH, Samadi N. Contradictory roles of Nrf2/Keap1 signaling pathway in cancer prevention/promotion and chemoresistance. DNA Repair 2017; 54: 13-21. [DOI:10.1016/j.dnarep.2017.03.008] [PMID]
27. Wasik U, Milkiewicz M, Kempinska-Podhorodecka A, Milkiewicz P. Protection against oxidative stress mediated by the Nrf2/Keap1 axis is impaired in primary biliary cholangitis. Sci Rep 2017; 7: 44769. [DOI:10.1038/srep44769] [PMID] [PMCID]
28. Acharyya S, Dutta S, Sengupta P. Adipokines as immune modulators in inflammation mediated male infertility. J Integr Sci Technol 2023; 11: 573.
29. Mansouri Torghabeh F, Rostamzadeh P, Davoudi S, Keivan M, Shokri‐Asl V. Effects of Rosmarinus officinalis on orchitis following spermatic cord torsion‐detorsion in male mice with emphasis on anti‐inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Andrologia 2022; 54: e14252. [DOI:10.1111/and.14252] [PMID]
30. Jannatifar R, Parivar K, Roodbari NH, Nasr-Esfahani MH. The effect of N-acetyl-cysteine on NRF2 antioxidant gene expression in asthenoteratozoospermia men: A clinical trial study. Int J Fertil Steril 2020; 14: 171-175.
31. Hu Z, Liu Q, Yan Z, Wang Q, Liu J. Protective effect of remote ischemic postconditioning in rat testes after testicular torsion/detorsion. Andrology 2022; 10: 973-983. [DOI:10.1111/andr.13184] [PMID]
32. Fang Y, Wang X, Yang D, Lu Y, Wei G, Yu W, et al. Relieving cellular energy stress in aging, neurodegenerative, and metabolic diseases, SIRT1 as a therapeutic and promising node. Front Aging Neurosci 2021; 13: 738686. [DOI:10.3389/fnagi.2021.738686] [PMID] [PMCID]
33. Ding Y-W, Zhao G-J, Li X-L, Hong G-L, Li M-F, Qiu Q-M, et al. SIRT1 exerts protective effects against paraquat-induced injury in mouse type II alveolar epithelial cells by deacetylating NRF2 in vitro. Int J Mol Med 2016; 37: 1049-1058. [DOI:10.3892/ijmm.2016.2503] [PMID]
34. Lee B-C, Kang K-S. Functional enhancement strategies for immunomodulation of mesenchymal stem cells and their therapeutic application. Stem Cell Res Ther 2020; 11: 397. [DOI:10.1186/s13287-020-01920-3] [PMID] [PMCID]
35. Hu C, Zhao L, Zhang L, Bao Q, Li L. Mesenchymal stem cell-based cell-free strategies: Safe and effective treatments for liver injury. Stem Cell Res Ther 2020; 11: 377. [DOI:10.1186/s13287-020-01895-1] [PMID] [PMCID]
36. Yan X, Fu X, Jia Y, Ma X, Tao J, Yang T, et al. Nrf2/Keap1/ARE signaling mediated an antioxidative protection of human placental mesenchymal stem cells of fetal origin in alveolar epithelial cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019; 2019: 2654910. [DOI:10.1155/2019/2654910] [PMID] [PMCID]
37. Zhong L, Yang M, Zou X, Du T, Xu H, Sun J. Human umbilical cord multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells alleviate acute ischemia-reperfusion injury of spermatogenic cells via reducing inflammatory response and oxidative stress. Stem Cell Res Ther 2020; 11: 294. [DOI:10.1186/s13287-020-01813-5] [PMID] [PMCID]
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |