Thu, Feb 26, 2026
[Archive]
Volume 22, Issue 7 (July 2024)
IJRM 2024, 22(7): 553-566 |
Back to browse issues page
Ethics code: IR.ARAKU.REC.1400.003
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Shariatzadeh S M A, Salmani F, Moghanlo H, Mahmoodi M. Stereological and biochemical effects of thymoquinone on ovarian tissue toxicity induced by silver nanoparticles in NMRI mice: An experimental study. IJRM 2024; 22 (7) :553-566
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-3301-en.html
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-3301-en.html
1- Department of Biology, Faculty of Sciences, Arak University, Arak, Iran. , s-shariatzadeh@araku.ac.ir
2- Department of Biology, Faculty of Sciences, Arak University, Arak, Iran.
2- Department of Biology, Faculty of Sciences, Arak University, Arak, Iran.
Abstract: (2585 Views)
Background: The toxicity of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) has been proven in the female reproductive system. Thymoquinone (TQ) is a natural antioxidant and bioactive component of Nigella sativa.
Objective: We evaluated the efficacy of TQ on ovarian tissue following toxicity induced by AgNPs in female mice.
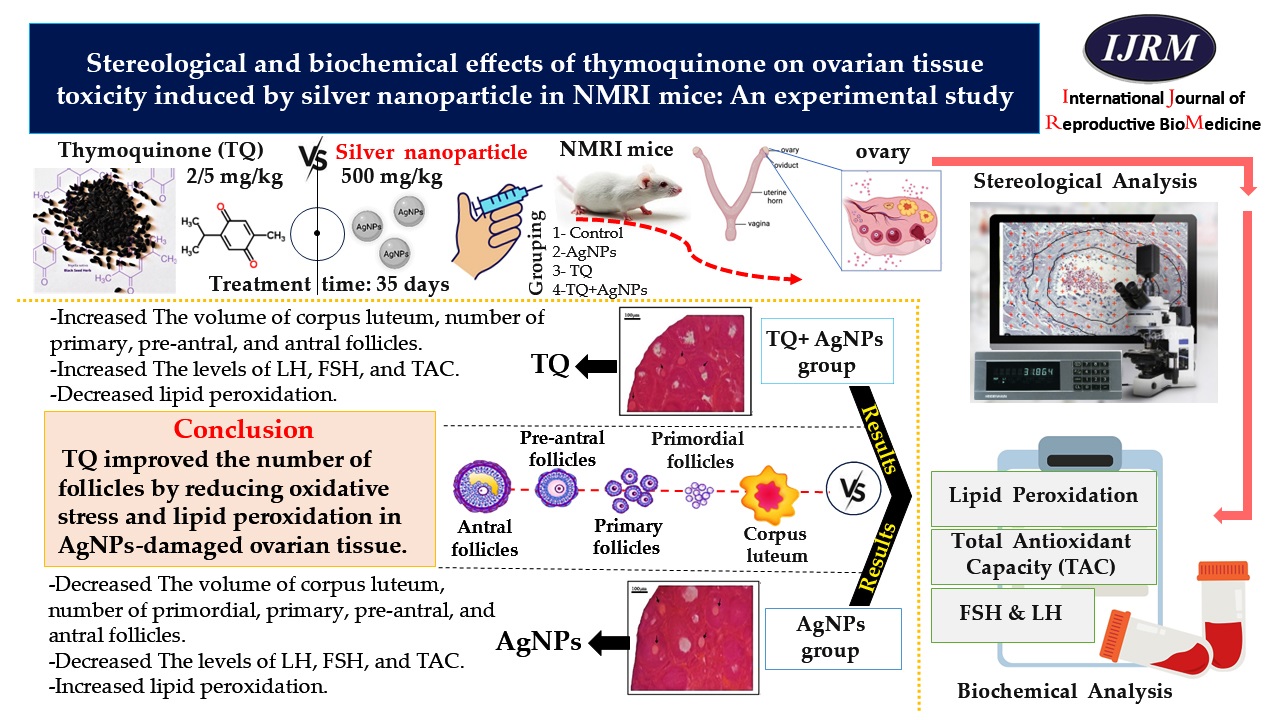
Materials and Methods: 24 female NMRI mice (5-6 wk, an average weight of 33 gr) were randomly divided into 4 groups (n = 6/each): control, AgNPs (500 mg/kg, gavage), TQ (2.5 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection), and TQ+AgNPs. Mice were treated every day for 35 days. Serum levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), total antioxidant capacity (TAC), luteinizing hormone, and follicle-stimulating hormone were measured. The optical disector and stereological techniques were utilized to estimate the follicular count, their volume at different developmental stages, and the structure of ovarian tissue.
Results: In the AgNPs group, the serum concentrations of TAC (p = 0.01), luteinizing hormone (p < 0.001), follicle-stimulating hormone, the volume of corpus luteum (p < 0.001), and the number of follicles decreased significantly compared to the control group. Nevertheless, AgNPs significantly increased the MDA level. In the TQ+AgNPs group compared to the AgNPs group, a significant decrease in MDA level (p < 0.001) and a significant improvement in TAC (p = 0.03), and hormonal levels, the number of primary, preantral, and antral follicles (p = 0.04), and the volume of corpus luteum (p = 0.01) were observed.
Conclusion: TQ improved the number of follicles by reducing oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation in AgNPs-damaged ovarian tissue.
Objective: We evaluated the efficacy of TQ on ovarian tissue following toxicity induced by AgNPs in female mice.
Materials and Methods: 24 female NMRI mice (5-6 wk, an average weight of 33 gr) were randomly divided into 4 groups (n = 6/each): control, AgNPs (500 mg/kg, gavage), TQ (2.5 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection), and TQ+AgNPs. Mice were treated every day for 35 days. Serum levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), total antioxidant capacity (TAC), luteinizing hormone, and follicle-stimulating hormone were measured. The optical disector and stereological techniques were utilized to estimate the follicular count, their volume at different developmental stages, and the structure of ovarian tissue.
Results: In the AgNPs group, the serum concentrations of TAC (p = 0.01), luteinizing hormone (p < 0.001), follicle-stimulating hormone, the volume of corpus luteum (p < 0.001), and the number of follicles decreased significantly compared to the control group. Nevertheless, AgNPs significantly increased the MDA level. In the TQ+AgNPs group compared to the AgNPs group, a significant decrease in MDA level (p < 0.001) and a significant improvement in TAC (p = 0.03), and hormonal levels, the number of primary, preantral, and antral follicles (p = 0.04), and the volume of corpus luteum (p = 0.01) were observed.
Conclusion: TQ improved the number of follicles by reducing oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation in AgNPs-damaged ovarian tissue.
Type of Study: Original Article |
Subject:
Reproductive Biology
References
1. Bala R, Singh V, Rajender S, Singh K. Environment, lifestyle, and female infertility. Reprod Sci 2021; 28: 617-638. [DOI:10.1007/s43032-020-00279-3] [PMID]
2. Liao Ch, Li Y, Tjong SC. Bactericidal and cytotoxic properties of silver nanoparticles. Int J Mol Sci 2019; 20: 449. [DOI:10.3390/ijms20020449] [PMID] [PMCID]
3. Burdușel A-C, Gherasim O, Grumezescu AM, Mogoantă L, Ficai A, Andronescu E. Biomedical applications of silver nanoparticles: An up-to-date overview. Nanomaterials 2018; 8: 681. [DOI:10.3390/nano8090681] [PMID] [PMCID]
4. Li Y, Cummins E. Hazard characterization of silver nanoparticles for human exposure routes. J Environment Sci Health Part A 2020; 55: 704-725. [DOI:10.1080/10934529.2020.1735852] [PMID]
5. Moghanlo H, Shariatzadeh SMA. Beneficial effects of Spirulina platensis on mice testis damaged by silver nanoparticles. Andrologia 2022; 54: e14606. [DOI:10.1111/and.14606] [PMID]
6. Zhang J, Wang F, Yalamarty SSK, Filipczak N, Jin Y, Li X. Nano silver-induced toxicity and associated mechanisms. Int J Nanomed 2022; 17: 1851-1864. [DOI:10.2147/IJN.S355131] [PMID] [PMCID]
7. Wang R, Song B, Wu J, Zhang Y, Chen A, Shao L. Potential adverse effects of nanoparticles on the reproductive system. Int J Nanomed 2018; 13: 8487-8506. [DOI:10.2147/IJN.S170723] [PMID] [PMCID]
8. Santacruz-Márquez R, Gonzalez-De los Santos M, Hernandez-Ochoa I. Ovarian toxicity of nanoparticles. Reprod Toxicol 2021; 103: 79-95. [DOI:10.1016/j.reprotox.2021.06.002] [PMID]
9. Zhang J, Liu S, Han J, Wang Z, Zhang S. On the developmental toxicity of silver nanoparticles. Mater Des 2021; 203: 109611. [DOI:10.1016/j.matdes.2021.109611]
10. Han JW, Jeong J-K, Gurunathan S, Choi Y-J, Das J, Kwon D-N, et al. Male-and female-derived somatic and germ cell-specific toxicity of silver nanoparticles in mouse. Nanotoxicology 2016; 10: 361-373. [DOI:10.3109/17435390.2015.1073396] [PMID]
11. Zhang D, Yu F, Li H, Wang Q, Wang M, Qian H, et al. AgNPs reduce reproductive capability of female mouse for their toxic effects on mouse early embryo development. Hum Exp Toxicol 2022; 41: 09603271221080235. [DOI:10.1177/09603271221080235] [PMID]
12. Mirzaei M, Razi M, Sadrkhanlou R. Nanosilver particles increase follicular atresia: Correlation with oxidative stress and aromatization. Environment Toxicol 2017; 32: 2244-2255. [DOI:10.1002/tox.22440] [PMID]
13. Hannan MA, Rahman MA, Sohag AAM, Uddin MJ, Dash R, Sikder MH, et al. Black cumin (Nigella sativa L.): A comprehensive review on phytochemistry, health benefits, molecular pharmacology, and safety. Nutrients 2021; 13: 1784. [DOI:10.3390/nu13061784] [PMID] [PMCID]
14. Sadeghi E, Imenshahidi M, Hosseinzadeh H. Molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways of black cumin (Nigella sativa) and its active constituent, thymoquinone: A review. Mol Biol Rep 2023; 50: 5439-5454. [DOI:10.1007/s11033-023-08363-y] [PMID]
15. Sarkar C, Jamaddar S, Islam T, Mondal M, Islam MT, Mubarak MS. Therapeutic perspectives of the black cumin component thymoquinone: A review. Food Function 2021; 12: 6167-6213. [DOI:10.1039/D1FO00401H] [PMID]
16. Darakhshan S, Pour AB, Colagar AH, Sisakhtnezhad S. Thymoquinone and its therapeutic potentials. Pharmacol Res 2015; 95: 138-158. [DOI:10.1016/j.phrs.2015.03.011] [PMID]
17. Alaee S, Mirani M, Derakhshan Z, Koohpeyma F, Bakhtari A. Thymoquinone improves folliculogenesis, sexual hormones, gene expression of apoptotic markers and antioxidant enzymes in polycystic ovary syndrome rat model. Vet Med Sci 2023; 9: 290-300. [DOI:10.1002/vms3.958] [PMID] [PMCID]
18. Sanamiri K, Mehranjani MS, Shahhoseini M, Shariatzadeh MA. L-carnitine improves follicular survival and function in ovarian grafts in the mouse. Reprod Fertil Dev 2022; 34: 713-721. [DOI:10.1071/RD21287] [PMID]
19. Rezvani E, Rafferty A, McGuinness C, Kennedy J. Adverse effects of nanosilver on human health and the environment. Acta Biomater 2019; 94: 145-159. [DOI:10.1016/j.actbio.2019.05.042] [PMID]
20. Mohamed Y, El Ghareeb A-W, Attaby FA, Abd El-Rahman HA. Estimation of silver nanoparticles effect on the reproductive health of female Wistar rats. Egypt J Basic Appl Sci 2022; 9: 340-358. [DOI:10.1080/2314808X.2022.2092821]
21. Pourali P, Nouri M, Ameri F, Heidari T, Kheirkhahan N, Arabzadeh S, et al. Histopathological study of the maternal exposure to the biologically produced silver nanoparticles on different organs of the offspring. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 2020; 393: 867-878. [DOI:10.1007/s00210-019-01796-y] [PMID]
22. Hou C-C, Zhu J-Q. Nanoparticles and female reproductive system: How do nanoparticles affect oogenesis and embryonic development. Oncotarget 2017; 8: 109799. [DOI:10.18632/oncotarget.19087] [PMID] [PMCID]
23. AL-ghamdi M, Huwait E, Elsawi N, Ali SS, Sayed A. Thymoquinone ameliorates acrylamide-induced reproductive toxicity in female rats: An experimental study. Int J Reprod BioMed 2023; 21: 61-70. [DOI:10.18502/ijrm.v21i1.12668] [PMID] [PMCID]
24. Saha P, Kumar S, Datta K, Tyagi RK. Upsurge in autophagy, associated with mifepristone-treated polycystic ovarian condition, is reversed upon thymoquinone treatment. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2021; 208: 105823. [DOI:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105823] [PMID]
25. Eini F, Bidadkosh A, Nazarian H, Piryaei A, Ghaffari Novin M, Joharchi K. Thymoquinone reduces intracytoplasmic oxidative stress and improves epigenetic modification in polycystic ovary syndrome mice oocytes, during in‐vitro maturation. Mol Reprod Dev 2019; 86: 1053-1066. [DOI:10.1002/mrd.23222] [PMID]
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |