Sat, Feb 21, 2026
[Archive]
Volume 22, Issue 12 (December 2024)
IJRM 2024, 22(12): 1003-1014 |
Back to browse issues page
Ethics code: IR.MUBABOL.REC.1401.050
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Nazari Hagh Y, Ahmadifard M, Esmaelzadeh S, abbaszadeh S, Shokrzadeh N. Decreased expression of miRNA-200a and miRNA-223-3p in endometriosis cases during the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle: insights from a comprehensive case-control study with analysis of molecular biomarkers and their potential role in disease-induced infertility.. IJRM 2024; 22 (12) :1003-1014
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-3306-en.html
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-3306-en.html
Yasaman Nazari Hagh1 

 , Mohamadreza Ahmadifard2
, Mohamadreza Ahmadifard2 

 , Sedigheh Esmaelzadeh3
, Sedigheh Esmaelzadeh3 

 , Soheila Abbaszadeh3
, Soheila Abbaszadeh3 

 , Naser Shokrzadeh *4
, Naser Shokrzadeh *4 




 , Mohamadreza Ahmadifard2
, Mohamadreza Ahmadifard2 

 , Sedigheh Esmaelzadeh3
, Sedigheh Esmaelzadeh3 

 , Soheila Abbaszadeh3
, Soheila Abbaszadeh3 

 , Naser Shokrzadeh *4
, Naser Shokrzadeh *4 


1- School of Medicine, Shahroud University of Medical Sciences, Shahroud, Iran.
2- Department of Medical Genetics, School of Medicine, Babol University of Medical Sciences, Babol, Iran.
3- Infertility and Reproductive Health Research Center, Health Research Institute, Babol University of Medical Sciences, Babol, Iran.
4- Reproductive Health Research Center, Clinical Research Institute, Urmia University of Medical Sciences, Urmia, Iran. ,shokrzadeh.n@umsu.ac.ir
2- Department of Medical Genetics, School of Medicine, Babol University of Medical Sciences, Babol, Iran.
3- Infertility and Reproductive Health Research Center, Health Research Institute, Babol University of Medical Sciences, Babol, Iran.
4- Reproductive Health Research Center, Clinical Research Institute, Urmia University of Medical Sciences, Urmia, Iran. ,
Abstract: (1030 Views)
Background: Endometriosis (EM) is a condition that causes infertility with decreasing uterine receptivity. It is reported that it affects about 20-25% of all infertile women. Some genetic markers play a crucial role in pathogenesis and infertility.
Objective: This study investigates the role of miR-200a and miR-223-3p in embryo implantation and their association with EM-related infertility.
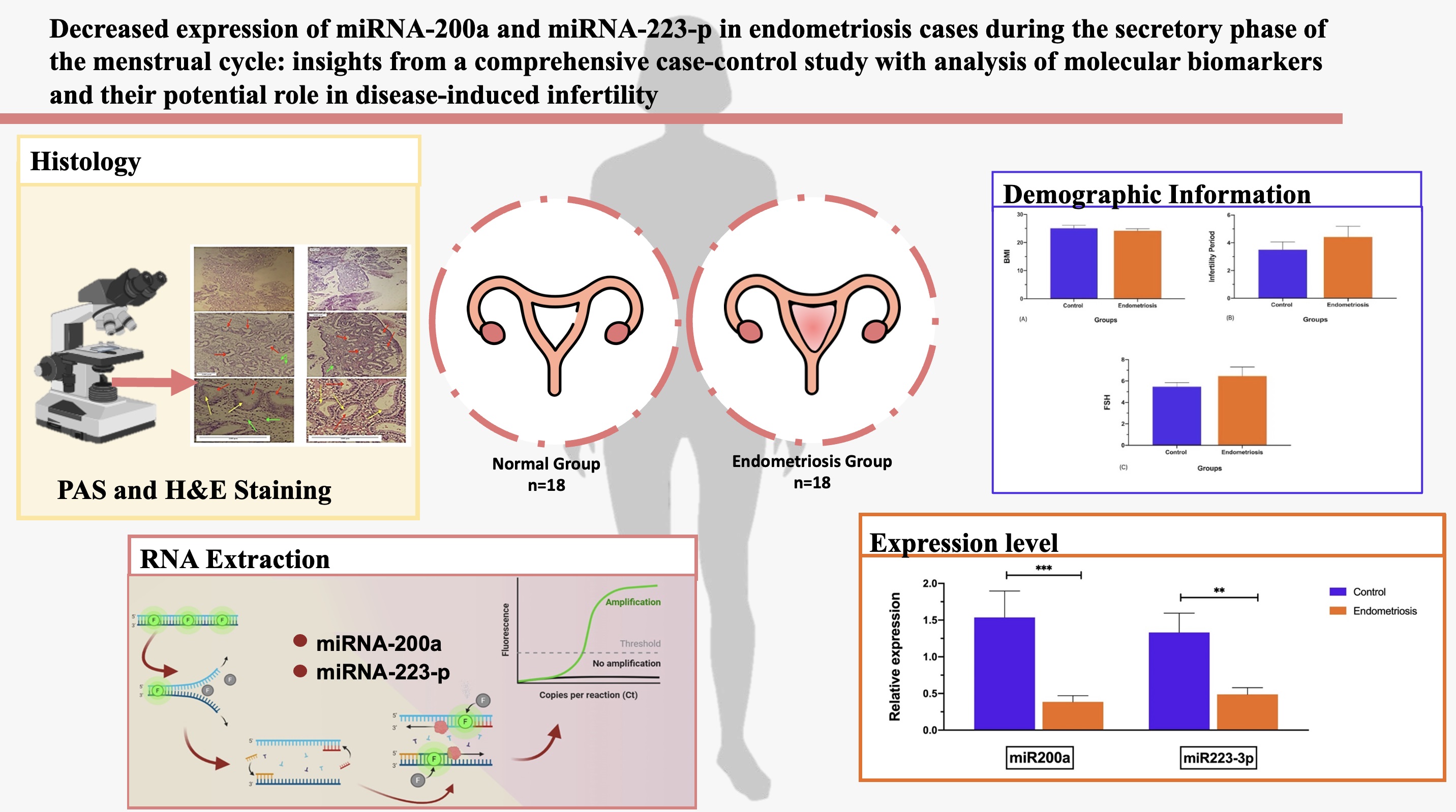
Materials and Methods: In this case-control study, 36 women who referred to the Center for Research on Reproductive Health and Infertility of Babol University of Medical Sciences and Fatemeh Al-Zahra Infertility Specialized Treatment Center in Babol, Iran between June 2022 and July 2023 were evaluated. Participants were divided into 2 EM and control groups (n = 18/each). Endometrial samples were collected from participants between 17th and 24th days of their menstrual cycle. Histopathological examination (hematoxylin and eosin and periodic acid schiff) was performed to confirm the secretory stage, and miR-200a and miR-223-3p expressions were analyzed by quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction.
Results: Histological analysis confirmed that both groups were in the secretory stage. Additionally, miRNA expression results showed a significant decrease in the miR-200a and miR-223-3p expression levels in EM group compared to control group. The expression level of miR-223-3p and miR-200a in the eutopic endometrial tissue of women with EM was notably lower than those in the control group.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that miR-200a and miR-223-3p are involved in the EM pathogenesis, while other genes and signaling pathways are probably involved in the implantation failure.
Objective: This study investigates the role of miR-200a and miR-223-3p in embryo implantation and their association with EM-related infertility.
Materials and Methods: In this case-control study, 36 women who referred to the Center for Research on Reproductive Health and Infertility of Babol University of Medical Sciences and Fatemeh Al-Zahra Infertility Specialized Treatment Center in Babol, Iran between June 2022 and July 2023 were evaluated. Participants were divided into 2 EM and control groups (n = 18/each). Endometrial samples were collected from participants between 17th and 24th days of their menstrual cycle. Histopathological examination (hematoxylin and eosin and periodic acid schiff) was performed to confirm the secretory stage, and miR-200a and miR-223-3p expressions were analyzed by quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction.
Results: Histological analysis confirmed that both groups were in the secretory stage. Additionally, miRNA expression results showed a significant decrease in the miR-200a and miR-223-3p expression levels in EM group compared to control group. The expression level of miR-223-3p and miR-200a in the eutopic endometrial tissue of women with EM was notably lower than those in the control group.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that miR-200a and miR-223-3p are involved in the EM pathogenesis, while other genes and signaling pathways are probably involved in the implantation failure.
This article has been extracted from M.Sc. Thesis. (Yasaman Nazari Hagh)
Keywords: Endometriosis, miRNA, Implantation, Signaling pathways, Biomarkers, Infertility, Menstrual cycle.
Type of Study: Original Article |
Subject:
Cellular and Molecular Biology of Reproduction
References
1. Cousins FL, McKinnon BD, Mortlock S, Fitzgerald HC, Zhang C, Montgomery GW, et al. New concepts on the etiology of endometriosis. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2023; 49: 1090-1105. [DOI:10.1111/jog.15549] [PMID] [PMCID]
2. Marquardt RM, Tran DN, Lessey BA, Rahman MS, Jeong J-W. Epigenetic dysregulation in endometriosis: Implications for pathophysiology and therapeutics. Endoc Rev 2023; 44: 1074-1095. [DOI:10.1210/endrev/bnad020] [PMID] [PMCID]
3. Balalau DO, Ciupitu IA, Bogheanu D-M, Ghiocel-Zariosu A-I, Balalau C, Ples L, et al. Management of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. J Mind Med Sci 2023; 10: 79-84. [DOI:10.22543/2392-7674.1390]
4. Da Broi MG, Ferriani RA, Navarro PA. Ethiopathogenic mechanisms of endometriosis-related infertility. JBRA Assist Reprod 2019; 23: 273-280. [DOI:10.5935/1518-0557.20190029] [PMID] [PMCID]
5. Lee D, Kim SK, Lee JR, Jee BC. Management of endometriosis-related infertility: Considerations and treatment options. Clin Exp Reprod Med 2020; 47: 1-11.
https://doi.org/10.5653/cerm.2020.47.1.1.e1 [DOI:10.5653/cerm.2019.02971]
6. Patel BG, Rudnicki M, Yu J, Shu Y, Taylor RN. Progesterone resistance in endometriosis: Origins, consequences and interventions. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2017; 96: 623-632. [DOI:10.1111/aogs.13156] [PMID]
7. Zhang P, Wang G. Progesterone resistance in endometriosis: Current evidence and putative mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci 2023; 24: 6992. [DOI:10.3390/ijms24086992] [PMID] [PMCID]
8. Marquardt RM, Kim TH, Shin J-H, Jeong J-W. Progesterone and estrogen signaling in the endometrium: What goes wrong in endometriosis? Int J Mol Sci 2019; 20: 3822. [DOI:10.3390/ijms20153822] [PMID] [PMCID]
9. Niknafs B, Shokrzadeh N, Alivand MR, Hesam Shariati MB. The effect of dexamethasone on uterine receptivity, mediated by the ERK1/2-mTOR pathway, and the implantation window: An experimental study. Int J Reprod BioMed 2022; 20: 47-58. [DOI:10.18502/ijrm.v20i1.10408] [PMID] [PMCID]
10. Shokrzadeh N, Alivand MR, Abedelahi A, Hessam Shariati MB, Niknafs B. Calcitonin administration improves endometrial receptivity via regulation of LIF, Muc‐1 and microRNA Let‐7a in mice. J Cell Physiol 2019; 234: 12989-13000. [DOI:10.1002/jcp.27969] [PMID]
11. Alves AR, Dias MF, Silvestre M. Endometrial fluid biomarkers and their potential as predictors of successful embryo implantation. BioMedicine 2023; 13: 1-8. [DOI:10.37796/2211-8039.1413] [PMID] [PMCID]
12. Shokrzadeh N, Alivand MR, Abedelahi A, Hessam Shariati MB, Niknafs B. Upregulation of HB‐EGF, Msx. 1, and miRNA Let‐7a by administration of calcitonin through mTOR and ERK1/2 pathways during a window of implantation in mice. Mol Reprod Dev 2018; 85: 790-801. [DOI:10.1002/mrd.23061] [PMID]
13. Zarei R, Nikpour P, Rashidi B, Eskandari N, Aboutorabi R. Evaluation of Muc1 gene expression at the time of implantation in diabetic rat models treated with insulin, metformin and pioglitazone in the normal cycle and ovulation induction cycle. Int J Fertil Steril 2020; 14: 218.
14. Paul AB, Sadek ST, Mahesan AM. The role of microRNAs in human embryo implantation: A review. J Assist Reprod Genet 2019; 36: 179-187. [DOI:10.1007/s10815-018-1326-y] [PMID] [PMCID]
15. Zhou W, Dimitriadis E. Secreted MicroRNA to predict embryo implantation outcome: From research to clinical diagnostic application. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020; 8: 586510. [DOI:10.3389/fcell.2020.586510] [PMID] [PMCID]
16. Azam INA, Wahab NA, Mokhtar MH, Shafiee MN, Mokhtar NM. Roles of microRNAs in regulating apoptosis in the pathogenesis of endometriosis. Life 2022; 12: 1321. [DOI:10.3390/life12091321] [PMID] [PMCID]
17. Cai H, Zhu X-X, Li Z-F, Zhu Y-P, Lang J-H. MicroRNA dysregulation and steroid hormone receptor expression in uterine tissues of rats with endometriosis during the implantation window. Chin Med J 2018; 131: 2193-2204. [DOI:10.4103/0366-6999.240808] [PMID] [PMCID]
18. Wilczynski M, Danielska J, Dzieniecka M, Szymanska B, Wojciechowski M, Malinowski A. Prognostic and clinical significance of miRNA-205 in endometrioid endometrial cancer. PLoS One 2016; 11: e0164687. [DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0164687] [PMID] [PMCID]
19. Liu Y, Chen J, Zhu X, Tang L, Luo X, Shi Y. Role of miR 449b 3p in endometriosis via effects on endometrial stromal cell proliferation and angiogenesis. Mol Med Rep 2018; 18: 3359-3365. [DOI:10.3892/mmr.2018.9341] [PMID] [PMCID]
20. Abel Y, Rederstorff M. Stem-Loop qRT-PCR-based quantification of miRNAs. Methods Mol Biol 2021; 2300: 59-64. [DOI:10.1007/978-1-0716-1386-3_6] [PMID]
21. Ohlsson Teague EMC, Van der Hoek KH, Van der Hoek MB, Perry N, Wagaarachchi P, Robertson SA, et al. MicroRNA-regulated pathways associated with endometriosis. Mol Endocrinol 2009; 23: 265-275. [DOI:10.1210/me.2008-0387] [PMID] [PMCID]
22. Filigheddu N, Gregnanin I, Porporato PE, Surico D, Perego B, Galli L, et al. Differential expression of microRNAs between eutopic and ectopic endometrium in ovarian endometriosis. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010; 2010: 369549. [DOI:10.1155/2010/369549] [PMID] [PMCID]
23. Jimenez PT, Mainigi MA, Word RA, Kraus WL, Mendelson CR. miR-200 regulates endometrial development during early pregnancy. Mol Endocrinol 2016; 30: 977-987. [DOI:10.1210/me.2016-1050] [PMID] [PMCID]
24. Gulyaeva LF, Kushlinskiy NE. Regulatory mechanisms of microRNA expression. J Transl Med 2016; 14: 143. [DOI:10.1186/s12967-016-0893-x] [PMID] [PMCID]
25. McGeary SE, Lin KS, Shi CY, Pham TM, Bisaria N, Kelley GM, et al. The biochemical basis of microRNA targeting efficacy. Science 2019; 366: eaav1741. [DOI:10.1126/science.aav1741] [PMID] [PMCID]
26. Górecki I, Rak B. The role of microRNAs in epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cancers; focusing on mir-200 family. Cancer Treat Res Commun 2021; 28: 100385. [DOI:10.1016/j.ctarc.2021.100385] [PMID]
27. Wu Y, Sun K, Tu Y, Li P, Hao D, Yu P, et al. miR‐200a‐3p regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and inflammation in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps by targeting ZEB1 via ERK/p38 pathway. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 2024; 14: 41-56. [DOI:10.1002/alr.23215] [PMID]
28. Roche J. The epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer. Cancers 2018; 10: 52. [DOI:10.3390/cancers10020052] [PMID] [PMCID]
29. Guo R, Hao G, Bao Y, Xiao J, Zhan X, Shi X, et al. MiR-200a negatively regulates TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of peritoneal mesothelial cells by targeting ZEB1/2 expression. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2018; 314: F1087-F1095. [DOI:10.1152/ajprenal.00566.2016] [PMID]
30. Shen L-J, He J-L, Yang D-H, Ding Y-B, Chen X-M, Geng Y-Q, et al. Mmu-microRNA-200a overexpression leads to implantation defect by targeting phosphatase and tensin homolog in mouse uterus. Reprod Sci 2013; 20: 1518-1528. [DOI:10.1177/1933719113488453] [PMID] [PMCID]
31. Xue Y, Lin X, Shi T, Tian Y. miRNA-223 expression in patient-derived eutopic and ectopic endometrial stromal cells and its effect on epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in endometriosis. Clinics 2022; 77: 100112. [DOI:10.1016/j.clinsp.2022.100112] [PMID] [PMCID]
32. Dong X, Sui C, Huang K, Wang L, Hu D, Xiong T, et al. MicroRNA-223-3p suppresses leukemia inhibitory factor expression and pinopodes formation during embryo implantation in mice. Am J Transl Res 2016; 8: 1155.
33. Niknafs B, Hesam Shariati MB, Shokrzadeh N. miR223‐3p, HAND2, and LIF expression regulated by calcitonin in the ERK1/2‐mTOR pathway during the implantation window in the endometrium of mice. Am J Reprod Immunol 2021; 85: e13333. [DOI:10.1111/aji.13333] [PMID]
34. Shariati MBH, Niknafs B, Seghinsara AM, Shokrzadeh N, Alivand MR. Administration of dexamethasone disrupts endometrial receptivity by alteration of expression of miRNA 223, 200a, LIF, Muc1, SGK1, and ENaC via the ERK1/2‐mTOR pathway. J Cell Physiol 2019; 234: 19629-19639. [DOI:10.1002/jcp.28562] [PMID]
35. You F, Du X, Zhang T, Wang Y, Lv Y, Zeng L. Electroacupuncture improves endometrial receptivity through miRNA-223-3p-mediated regulation of leukemia inhibitory factor/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling pathway. Bioengineered 2022; 13: 10298-10312. [DOI:10.1080/21655979.2022.2062524] [PMID] [PMCID]
36. Tang Y, Wang Y, Chen Q, Qiu N, Zhao Y, You X. MiR-223 inhibited cell metastasis of human cervical cancer by modulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015; 8: 11224.
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |