Sun, Feb 15, 2026
[Archive]
Volume 23, Issue 12 (December 2025)
IJRM 2025, 23(12): 985-994 |
Back to browse issues page
Ethics code: No. 39 of May 22, 2014
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Efremova O, Ponomarenko I, Churnosov M, Efremova O. Association of polymorphic loci of the matrix metalloproteinase genes with the development of fetal growth retardation: A case-control study. IJRM 2025; 23 (12) :985-994
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-3570-en.html
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-3570-en.html
1- Department of Biomedical Disciplines, Belgorod State National Research University, Belgorod, Russia. , efremovaolesya@gmail.com; efremova@bsuedu.ru
2- Department of Biomedical Disciplines, Belgorod State National Research University, Belgorod, Russia.
3- Department of Faculty Therapy, Belgorod State National Research University, Belgorod, Russia.
2- Department of Biomedical Disciplines, Belgorod State National Research University, Belgorod, Russia.
3- Department of Faculty Therapy, Belgorod State National Research University, Belgorod, Russia.
Abstract: (34 Views)
Background: Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) play a crucial role in successful pregnancy as molecular regulatory factors of the developing organism. Additional studies focusing on MMPs activity and function in fetal growth retardation (FGR) may help in the search for diagnostic markers of this pregnancy complication.
Objective: To study the association of MMPs gene polymorphisms with the development of FGR.
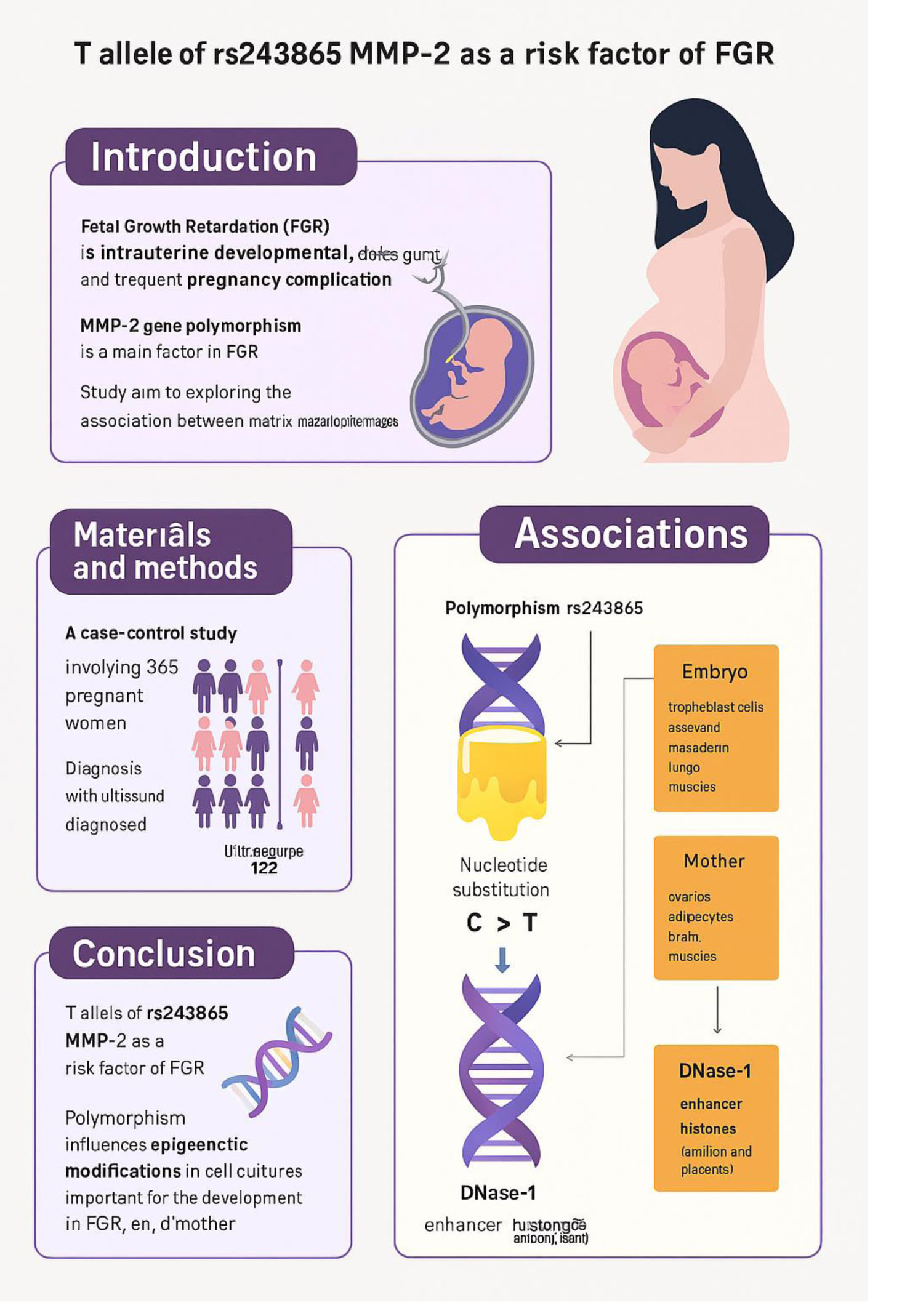
Materials and Methods: This case-control study included 122 pregnant women with FGR and 243 pregnant women with normal birth weight. We studied polymorphic loci of metalloproteinase genes: rs1799750 of MMP-1, rs243865 of MMP-2, rs3025058 of MMP-3, rs11568819 of MMP-7, rs17577 of MMP-9. The polymorphism study was performed by TaqMan probe detection using real-time precipitation reaction. The logistic regression method was used to analyze the association of polymorphisms with FGR.
Results: The T allelic variant rs243865 of the MMP-2 gene was found to be associated with the development of FGR under allelic (odds ratio [OR] = 1.56, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.08-2.24, pperm = 0.016), additive (OR = 1.53, 95% CI: 1.07-2.18, pperm = 0.015) and dominant (OR = 1.61, 95% CI: 1.03-2.50, pperm = 0.027) models. The FGR-causative locus rs243865 of MMP-2 is located in the enhancer region in the amnion and placenta tissues, affects epigenetic modifications in FGR-significant cell/organ cultures both in the embryo/fetus in the maternal body and in the mother's body, changes deoxyribonucleic acid binding affinity to the myogenic factor transcription, transcriptional activity of RP11-212I21.2 gene in arteries.
Conclusion: The T allele rs243865 of the MMP-2 gene was found to be a risk factor for the development of FGR.
Objective: To study the association of MMPs gene polymorphisms with the development of FGR.
Materials and Methods: This case-control study included 122 pregnant women with FGR and 243 pregnant women with normal birth weight. We studied polymorphic loci of metalloproteinase genes: rs1799750 of MMP-1, rs243865 of MMP-2, rs3025058 of MMP-3, rs11568819 of MMP-7, rs17577 of MMP-9. The polymorphism study was performed by TaqMan probe detection using real-time precipitation reaction. The logistic regression method was used to analyze the association of polymorphisms with FGR.
Results: The T allelic variant rs243865 of the MMP-2 gene was found to be associated with the development of FGR under allelic (odds ratio [OR] = 1.56, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.08-2.24, pperm = 0.016), additive (OR = 1.53, 95% CI: 1.07-2.18, pperm = 0.015) and dominant (OR = 1.61, 95% CI: 1.03-2.50, pperm = 0.027) models. The FGR-causative locus rs243865 of MMP-2 is located in the enhancer region in the amnion and placenta tissues, affects epigenetic modifications in FGR-significant cell/organ cultures both in the embryo/fetus in the maternal body and in the mother's body, changes deoxyribonucleic acid binding affinity to the myogenic factor transcription, transcriptional activity of RP11-212I21.2 gene in arteries.
Conclusion: The T allele rs243865 of the MMP-2 gene was found to be a risk factor for the development of FGR.
Type of Study: Original Article |
Subject:
Pregnancy Health
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |