Sun, Feb 15, 2026
[Archive]
Volume 23, Issue 12 (December 2025)
IJRM 2025, 23(12): 1007-1020 |
Back to browse issues page
Ethics code: IR.KMU.REC.1402.071
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Asadollahi Z, Ghaheri A, Haji-Maghsoudi S, Haghdoost A, Ashrafi M, Eftekhari-Yazdi P et al . Determining factors associated with the number of oocytes with appropriate morphology in infertile women: A cross-sectional study. IJRM 2025; 23 (12) :1007-1020
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-3615-en.html
URL: http://ijrm.ir/article-1-3615-en.html
Zahra Asadollahi1 

 , Azadeh Ghaheri2
, Azadeh Ghaheri2 

 , Saiedeh Haji-Maghsoudi3
, Saiedeh Haji-Maghsoudi3 

 , AliAkbar Haghdoost4
, AliAkbar Haghdoost4 

 , Mahnaz Ashrafi5
, Mahnaz Ashrafi5 

 , Poopak Eftekhari-Yazdi6
, Poopak Eftekhari-Yazdi6 

 , Yunes Jahani *7
, Yunes Jahani *7 




 , Azadeh Ghaheri2
, Azadeh Ghaheri2 

 , Saiedeh Haji-Maghsoudi3
, Saiedeh Haji-Maghsoudi3 

 , AliAkbar Haghdoost4
, AliAkbar Haghdoost4 

 , Mahnaz Ashrafi5
, Mahnaz Ashrafi5 

 , Poopak Eftekhari-Yazdi6
, Poopak Eftekhari-Yazdi6 

 , Yunes Jahani *7
, Yunes Jahani *7 


1- Modeling in Health Research Center, Institute for Futures Studies in Health, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran. & Department of Biostatistics and Epidemiology, School of Public Health, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran., Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Rafsanjan University of Medical Sciences, Rafsanjan, Iran.
2- Department of Basic and Population Based Studies in NCD, Reproductive Epidemiology Research Center, Royan Institute, ACECR, Tehran, Iran.
3- Modeling in Health Research Center, Institute for Futures Studies in Health, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran. & Department of Biostatistics and Epidemiology, School of Public Health, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran.
4- Medical Informatics Research Center, Institute for Futures Studies in Health, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran. & HIV/STI Surveillance Research Center, WHO Collaborating Center for HIV Surveillance, Institute for Futures Studies in Health, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran.
5- Department of Endocrinology and Female Infertility, Reproductive Biomedicine Research Center, Royan Institute for Reproductive Biomedicine, ACECR, Tehran, Iran.
6- Department of Embryology, Reproductive Biomedicine Research Center, Royan Institute for Reproductive Biomedicine, ACECR, Tehran, Iran.
7- Health in Disasters and Emergencies Research Center, Institute for Futures Studies in Health, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran. & Modeling in Health Research Center, Institute for Futures Studies in Health, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran., Department of Biostatistics and Epidemiology, School of Public Health, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran. ,yonesjahani@yahoo.com; u.jahani@kmu.ac.ir
2- Department of Basic and Population Based Studies in NCD, Reproductive Epidemiology Research Center, Royan Institute, ACECR, Tehran, Iran.
3- Modeling in Health Research Center, Institute for Futures Studies in Health, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran. & Department of Biostatistics and Epidemiology, School of Public Health, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran.
4- Medical Informatics Research Center, Institute for Futures Studies in Health, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran. & HIV/STI Surveillance Research Center, WHO Collaborating Center for HIV Surveillance, Institute for Futures Studies in Health, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran.
5- Department of Endocrinology and Female Infertility, Reproductive Biomedicine Research Center, Royan Institute for Reproductive Biomedicine, ACECR, Tehran, Iran.
6- Department of Embryology, Reproductive Biomedicine Research Center, Royan Institute for Reproductive Biomedicine, ACECR, Tehran, Iran.
7- Health in Disasters and Emergencies Research Center, Institute for Futures Studies in Health, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran. & Modeling in Health Research Center, Institute for Futures Studies in Health, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran., Department of Biostatistics and Epidemiology, School of Public Health, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran. ,
Abstract: (31 Views)
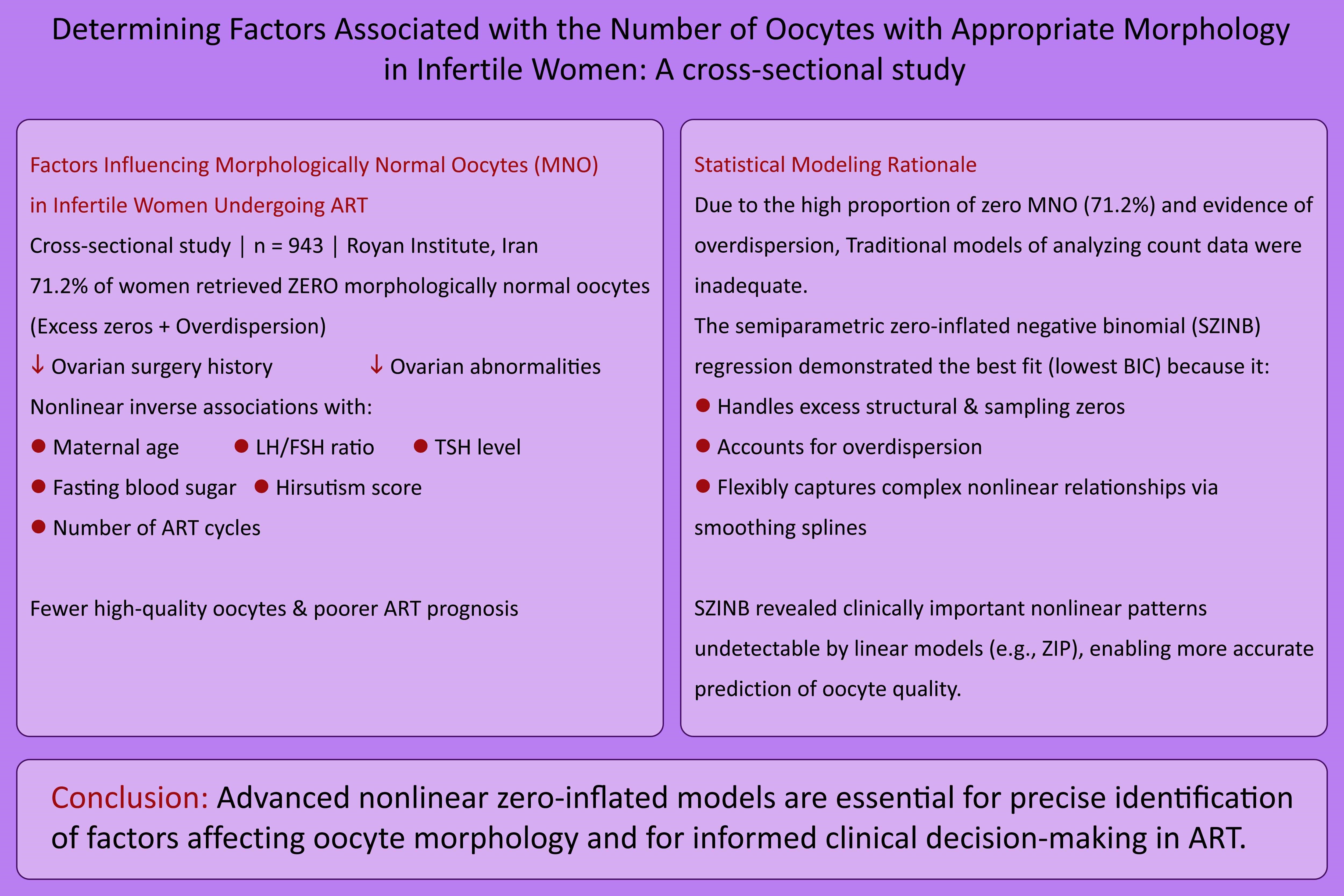
Background: Infertility affects millions of couples worldwide. The number of morphologically normal oocytes (MNO) is a key determinant of assisted reproductive technology success. Accurate identification of influencing factors is limited by excess zeros in real-world clinical data.
Objective: This study aimed to identify clinical factors associated with MNO count and to demonstrate the superiority of advanced statistical models, zero-inflated Poisson and semiparametric zero-inflated negative binomial regression, in analyzing high-quality clinical data with a high proportion of zeros.
Materials and Methods: In this cross-sectional study, data of 950 infertile women who referred to the Royan Institute, Tehran, Iran, between January 2012 and December 2013 were extracted from their medical records. Zero-inflated Poisson and semiparametric zero-inflated negative binomial regression models were used to count data with a large number of zeros.
Results: Ovarian surgery history (p = 0.045) and ovarian abnormalities (p = 0.041) significantly reduced MNO. Nonlinear inverse associations were observed with advancing age (p = 0.038), elevated luteinizing hormone/follicle-stimulating hormone ratio (p = 0.044), thyroid-stimulating hormone (p = 0.026), fasting blood sugar (p = 0.049), hirsutism score (p = 0.049), and increasing assisted reproductive technology cycles (p = 0.037). The semiparametric model provided the best fit and revealed complex nonlinear patterns not detectable by linear models.
Conclusion: The results of this study enhance our understanding of the clinical and hormonal factors influencing oocyte morphology in infertile women and highlight the importance of applying advanced nonlinear statistical models in reproductive medicine research.
Objective: This study aimed to identify clinical factors associated with MNO count and to demonstrate the superiority of advanced statistical models, zero-inflated Poisson and semiparametric zero-inflated negative binomial regression, in analyzing high-quality clinical data with a high proportion of zeros.
Materials and Methods: In this cross-sectional study, data of 950 infertile women who referred to the Royan Institute, Tehran, Iran, between January 2012 and December 2013 were extracted from their medical records. Zero-inflated Poisson and semiparametric zero-inflated negative binomial regression models were used to count data with a large number of zeros.
Results: Ovarian surgery history (p = 0.045) and ovarian abnormalities (p = 0.041) significantly reduced MNO. Nonlinear inverse associations were observed with advancing age (p = 0.038), elevated luteinizing hormone/follicle-stimulating hormone ratio (p = 0.044), thyroid-stimulating hormone (p = 0.026), fasting blood sugar (p = 0.049), hirsutism score (p = 0.049), and increasing assisted reproductive technology cycles (p = 0.037). The semiparametric model provided the best fit and revealed complex nonlinear patterns not detectable by linear models.
Conclusion: The results of this study enhance our understanding of the clinical and hormonal factors influencing oocyte morphology in infertile women and highlight the importance of applying advanced nonlinear statistical models in reproductive medicine research.
Keywords: Oocytes, Infertility, Female, Assisted reproductive technology, Regression analysis, Statistical models.
Type of Study: Original Article |
Subject:
Fertility & Infertility
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |